Database Reference
In-Depth Information
T
able 7.2.
Correspondences between knowledge and networks.
Knowledge base
Neural network
Final conclusions
Output neurons
Facts
Input neurons
Intermediate conclusions
Hidden neurons
Dependencies
Weight connections
structure, which creates the feature used in the example-based learning system.
Therefore, the created networks will have no derived feature that indicates
contextual dependencies or other useful conjunctions within example descriptions.
2. Mapping. The second step establishes a mapping between a transformed rule set
and a neural network, as shown in Table 7.2. This step can create a network that
has a one-to-one correspondence with the rule set.
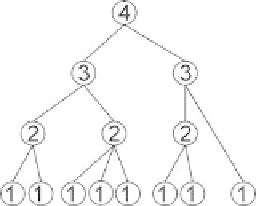
3. Numbering. This step numbers neurons in the network to define the level of
each neuron as the length of the longest path to the input neurons, as shown in Fig.
7.2.
4. Adding hidden neurons. This step adds hidden neurons to the network, giving
the network the ability to learn derived features that are not specified in the initial
rule set but are suggested by the expert, as shown in Fig. 7.3.
Fig.7.2.
Numbering neurons.
Fig.7.3.
Adding hidden neurons.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search