Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
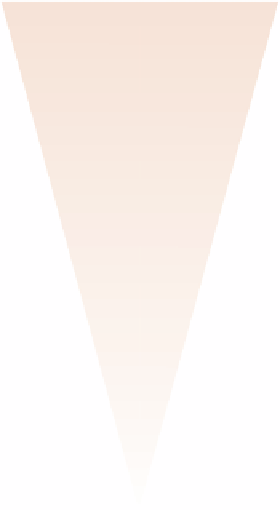
Fig. 2.6
ALARP model of risk level
order to safety assurance of the developed system may be certified as safe, there
must be a set of documents, which provides detail justification of the safety. This
document contains a list of all hazard's cases with log details and various arguments
for indicating that how the system has reached at the required safety levels. The
safety case brings in all the aforementioned risk analyses, risk reductions and other
integrity and reliability measures, often presenting various statistical evidence. It is
a considerable huge amount of a task involves lots of documentation. A software
SAM (Safety Arguments Manager) is recognised to support this process and allows
to manage all the developing safety cases [
82
].
2.6 Traditional System Engineering Approach
A critical system uses a standard life-cycle to achieve a certificate from the standard
authorities [
18
,
33
,
54
,
58
]. A system can be considered safe if all the hazards have
been eliminated, or the risk associated hazards have been reduced to an acceptable
level. Software is a part of a system, which is used within the system to operate the
system safely. The integrated software within a system does not show any kind of
misbehaviour. However, if the same software is used by multiple systems then the
software must have similar behaviour in each system. However, sometimes it is not
true. It is believed that each system is different, with different requirements, different




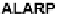














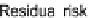




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search