Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 10.3
Abstract
representation
circles and arrows represent the next level of refinement for further analysing of any
particular diseases according to the guidelines and protocol.
Our abstract Event-B model of the ECG interpretation protocol assesses the
rhythm
and
heart rate
to distinguish between normal and abnormal heart. Fig-
ure
10.4
presents a basic diagram of the ECG analysis at an abstract level according
to the standard procedure of the ECG protocol analysis. The specification consists
of just three-state variables (
inv
1-
int
3)
Sinus
,
Heart_Rate
and
Heart_State
.The
Si-
nus
variable is represented by
YesNoState
as enumerated sets. The last two variables
Heart_Rate
and
Heart_State
are introduced as to show the heart rate limit and heart
states. One possible approach is to introduce a set of variables (
RR_Int_equidistant
,
PP_Int_equidistant
,
P_Positive
,
PP_Interval
and
RR_Interval
) representing total
functions mapping leads (LEADS) to a standard data type (
BOOL
,
) in invariants
(
inv
4-
inv
8). The RR and PP equidistant intervals in the ECG signal are represented
by variables
RR_Int_equidistant
and
PP_Int_equidistant
as the total functions from
LEADS
to
BOOL
.The
RR_Int_equidistant
and
PP_Int_equidistant
are functions,
which represent RR and PP equidistant interval's states in a boolean form. A vari-
able
P_Positive
represents a positive wave of the signal also as a total function from
LEADS
to
BOOL
.The
P_Positive
function is used to show the positive visualisation
of the P-waves. The next variables PP and RR intervals in the ECG signal are rep-
resented by the variables
PP_Interval
and
RR_Interval
as the total functions from
N
Fig. 10.4
Basic diagram of assessing rhythm and rate (adapted from [
16
])

















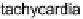
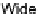











Search WWH ::

Custom Search