Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
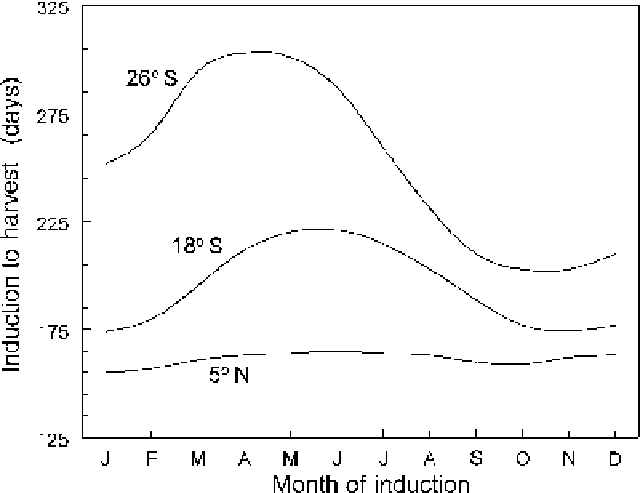
Fig. 12.3.
Effect of latitude as an indicator of solar radiation and temperature on the
time from forcing to harvest, 26° S is for Nambour, Australia, 18° S is Madagascar
and 5° N is Ivory Coast.
the responsiveness to fl ower-inducing compounds (Bartholomew
et al.
, 2003)
and shorten the time to fl oral induction under a short-day regime. High
temperatures (>28°C) make chemical fl ower induction more dii cult, with the
percentage of plants forced decreasing linearly with increasing temperature.
In Mexico between June and August, and in Thailand in most months of the
year, fruit produced for processing generally have low acidity and total soluble
solids (TSS). In Mexico, this lower quality is due to the combined ef ect of high
temperature, excessive rain and an increased number of cloudy days, while in
Thailand the response is due primarily to overly warm temperatures.
The 'Smooth Cayenne' group is the more productive in tropical conditions,
while the 'Queen' group is grown mainly in subtropical areas. 'Smooth
Cayenne' is most sensitive to low-temperature-induced internal browning
(chilling injury, blackheart), while 'Red Spanish' is less sensitive.
Sunlight
Most pineapple is grown in regions with high insolation, at least in part
because the crop is well adapted to areas with low rainfall. While the light level
required to saturate photosynthesis of a pineapple leaf is believed to be less
than 25% of full sunlight, high irradiance is required to sustain the high levels
of productivity found in commercial plantations, where plant population