Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CLJ
SLJ
HLJ
1.5k
1.0k
0.5k
=0.10
=0.10
=0.10
0
1.5k
=0.50
=0.50
=0.50
1.0k
0.5k
0
0.6k
=0.75
=0.75
=0.75
0.4k
0.2k
0
1k
2k
3k
1k
2k
3k
1k
2k
3k
time
time
time
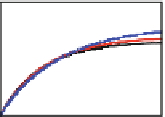
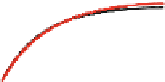
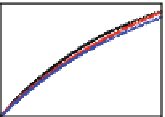
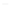
Fig. 3
(Color online) Confinement effect on the mean-square displacement (MSD).
Rows
shows
three representative densities (
ˁ
∗
=
.
,
.
.
75).
Columns
show the studied interaction
potentials, classic Lenard-Jones (CLJ), soft Lenard-Jones (SLJ) and hard repulsive potential (HLJ)
0
1
0
5and0
0
1, first row) and for long times, the MSD tend to a constant value since particles
have visited all the cavity area, therefore this plateau is a confinement effect. There
is also a small effect of the cavity shape on the MSD for all the interaction potentials.
We see that the magnitude of the MSD decreases in the following cavity shape
sequence: triangular, square and circular. This trend can be easily understood since
the maximum traveling distance (from the center of the cavity to its walls) occurs
inside a triangle, followed by a square and finally by a circle (see Table
1
showing
the relevant parameters of the cavities).
For
ˁ
∗
=
.
.
5, we can see a similar behavior between particles interacting with a
CLJ and a SLJ, however, we observe that particles interactingwith aHLJ and confined
in a triangular cavity, reduce their MSD. This case can be explained as follows. HLJ
originates hard collisions among particles, which reduce the speed of the spheres,
resulting in more free space inside the cavity and smaller MSD compared with the
SLJ. In the SLJ, collisions will not be so hard thus allowing to keep the speed of the
spheres high, resulting in less free space and higher MSD. This situation is visually
shown in Fig.
4
where particles inside a triangular shape and colliding by means of
a HLJ, produce more free space (see Fig.
4
b) compared with particles interacting by
means of SLJ (see Fig.
4
a). Note that for this density, the MSD has not yet reached
a constant value (see Fig.
3
, second row).
For
ˁ
∗
=
0
75 we observe in general a reduction of the system diffusion compared
with the lower density cases due to a decrease of free space. The case
ˁ
∗
0
.
=
0
.
75











































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search