Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ʻ
T
is a constant temperature, since
this study is based on the average normal human body temperature of 37
ⓦ
C and
considering that thermal damage occurs around the 42
ⓦ
C Torvi and Dale (
1994
),
this constant must not exceed from 5
ⓦ
C. Finally
∈
(
)
where
t
is the discrete stochastic variation.
˃
i
is the stochastic parameter which
takes values of 0
1. As the temperature only depends on time, the set of
equations generated can be numerically integrated by using the following initial
condition:
<
˃
i
<
˄
=
0
,
(ʾ, ʷ)
=
0
,
(7)
t
3 Results and Discussion
The solution of the model was discretized using a second-order central difference
formulation for all the spatial derivatives, with an explicit method and uniform grid
of 100
100. The numerical simulations were generated by a code developed in the
programming language Fortran, Ripley (
1987
).
×
3.1 Steady State Temperature
The first case is used to verify the numerical code and as reference model. It considers
a uniform heat source, which represents the conditions when the tissue is in thermal
equilibriumwith the surroundings. Factors affecting this state are due to themetabolic
activities and to the energy exchangewith the environment, this justifies using theBiot
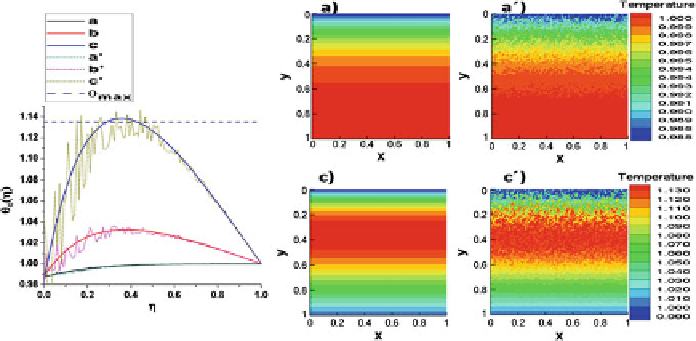
number as reference. The temperature distribution is shown in Fig.
2
, alongside with
Fig. 2
Temperature distributions in steady state with different Biot numbers and forms of metabolic
heat.
a
Bio
=
0.2,
∅
m
=
0
.
038,
b
Bio
=
1.3,
∅
m
=
1
.
4554,
c
Bio
=
1.3,
∅
m
=
5
.
2903

Search WWH ::

Custom Search