Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1 Introduction
This work is based on the theoretical work developed by Kurdyumov and Liñán
(
2001
) who studied the effects of the forced convection acting on a heated horizontal
cylinder that is buried in a fluid-saturated porous medium. Problems that involve both
free and forced convection due to a heat source,
q
, in a porous medium have been
studied theoretically by several authors (Wesseling
1974
; Bejan
1978
; Poulikakos
1984
; Pop and Ingham
2001
).
On the other hand, to our knowledge, there are few experimental studies aimed
to reproduce and observe the development of the laminar thermal plumes due to the
action of free and forced convection. In this work we use thermography techniques
(Astarita and Carlomagno
2013
) to experimentally study several configurations; an
infrared camera allows us to see the isotherms due to the convection process along
a transverse face of the porous medium. Detailed properties of the buoyant plumes
will be discussed after the theoretical elucidation of the problem and the description
of the experimental setup.
2 Theoretical Model
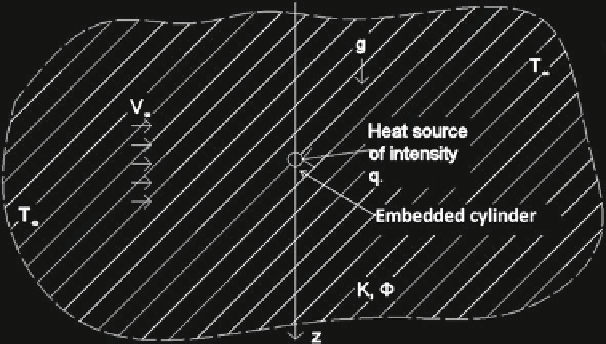
Consider an horizontal long and infinitesimal heated cylinder embedded in an
unbounded and fluid-saturated porous medium with permeability K and porosity
ˆ
. The heated cylinder yields a constant heat flow of intensity
q
to the homogeneous
unconfined porous medium, and a laminar air stream of velocity
V
∞
can be induced,
pointing towards the heat source, as it can be seen in Fig.
1
.
Fig. 1
Schematic transversal view of an
horizontal
heated cylinder embedded in a fluid saturated
porous medium. The temperature far from the cylinder is
T
∞
. A uniform stream comes to the
cylinder at velocity
V
∞

Search WWH ::

Custom Search