Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
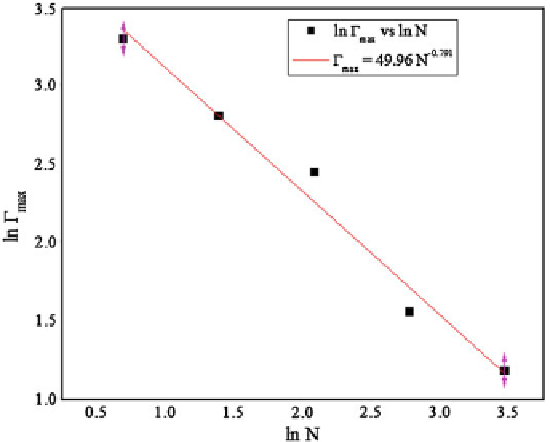
Fig. 12
Scaling of
ʳ
max
(maximum adsorption) with
N
for polyacrylic acid on
TiO
2
surfaces.
Taken from Mayoral and Nahmad-Achar (
2014
)
ʓ
max
versus
N
is
plotted, the behaviour shown in Fig.
12
is obtained and the scaling function is
N
and fitting each simulation to a Langmuir isotherm. When
ʓ
max
∝
N
−
4
/
5
. This result is in perfect agreement with the scaling theory in
the weak adsorption regime (de Gennes
1976
), which indicates that at maximum
saturation
N
−
0
.
79
∼
N
1
/
5
ʳ
p
=
ʓ
max
N
∼
,
(48)
where
ʳ
p
is the number of monomers adsorbed in the flat plateau of the isotherm.
This implies
N
−
0
.
8
as obtained above.
Finally, another important example could be found in Gama Goicochea et al.
(
2014
), where scaling laws for the viscosity (
ʷ
) and the friction coefficient (
μ
)were
obtained by non-equilibrium DPD simulations.
N
−
4
/
5
ʓ
max
∼
=
6 Conclusions
The appropriate parametrisation for the relevant parameters in Dissipative Particle
Dynamics (DPD) simulations were presented. A clear methodology has been devel-
oped in the last few years to obtain the interaction parameters in great detail for realis-
tic systems, making possible the study of their dependence on concentration and tem-
perature. This work has proven to give predictions in accordance with experimental
results. Explicit examples of interfacial tension, adsorption isotherms, disjoining
Search WWH ::

Custom Search