Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2
The Results of Angles Detection of Insulators in Complex Background
Take aerial insulator image with complex background (Im 3) as an example, the
results of angle detection of insulator are as following:
In Fig. 12, (a) is Im 3 with complex aerial background including tower, power
lines and vegetation, and (b) is its binary image with smooth and clear edges after
preprocessing.
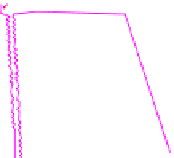
Extract the contours of Im 3 shown in Fig. 13(a). The concave-Convex and irregu-
lar curve contour would be approximated by a large number of line segments shown
in Fig. 13(b). Thus the points in each contour can be formed as a list of connected
edge points.
Compute the angle of each point and all the angles are composed of a set of se-
quential angular variation, and define the points with sign-Changing angle as candi-
date points. Fig. 14(a) shows candidate points of each connected contour in Im 3. All
candidate points can be extracted including some error points, and the accurate points
can be picked up by RANSAC shown in Fig. 14(b), and the straight line which points
locate in is the main direction of insulator.
After iterations, the orientation angles of all the connected contours can be detected
finally.
(a) (b)
Fig. 12.
Im 3 and its binary image after preprocessing. (a) Im 3. (b) Its binary image after pre-
processing.
(a) (b)
Fig. 13.
Curve edge of Im 3 and processed edge. (a) Curve edge of Im 3. (b) Processed edge.






























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search