Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
T
∂
S
∂
S
H
=
∇
B
⇅
⇅
∇
B
⇅
R
nr
nr
∂
d
∂
d
(8)
X
R
R
T
∂
S
[
]
()
(
( )
)
ʔ
d
=
H
−
1
⇅
∇
B
⇅
B
X
−
B
A
X
;
d
L
L
nl
pl
nl
L
∂
d
(9)
X
L
And
H
L
is the
Hessian matrix:
2
×
2
T
∂
S
∂
S
H
=
∇
B
⇅
⇅
∇
B
⇅
L
nl
nl
∂
d
∂
d
(10)
X
L
L
2.4
Reconstruct and Track the Whole Surface
After all correspondences of blocks are found in four images, reconstruction and
tracking of block surfaces can be independently obtained through the parameters of
each block correspondence, then the reconstructed block surfaces can be integrated
into one integral surface. However, because the parameters may be different between
different neighboring blocks, gaps may exist between the reconstructed surfaces of
neighboring blocks, which leads to the reconstructed unsmoothed surface. To solve
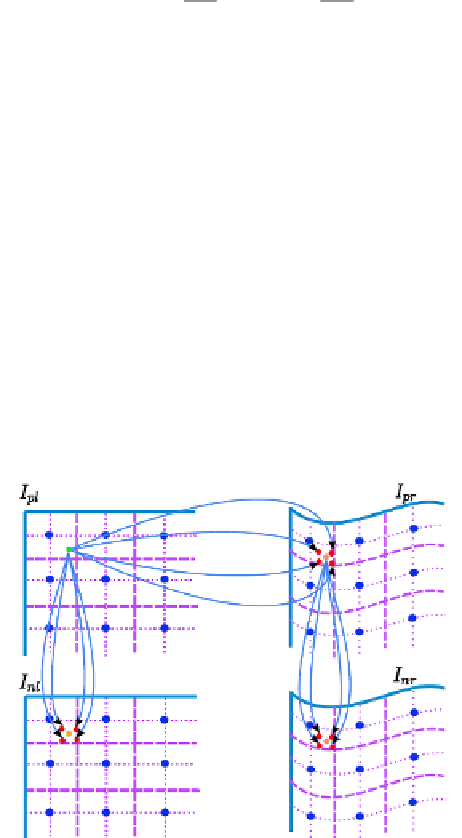
this problem, a bilinear interpolation method is adopted, as Fig.2 shows.
Fig. 2.
Interpolation method of reconstruction and tracking
Bilinear Interpolation. Figure2 illustrates the bilinear interpolation method for
smoothing reconstructed surface. For every four neighboring blocks in the template
image
I
pl
,
we consider the rectangle whose four vertices are composed of the centers
of the four neighboring blocks, in which one point should be influenced by the
parameters of the four neighboring blocks when transformation is carried out. As a
result, four corresponding points in image
I
pr
can be generated by the affine
parameters of the four neighboring blocks for every point in the rectangle. However,
due to the different values of the parameters of the four neighboring blocks, the
corresponding points in the image
I
pr
may be different from each other. In order to


Search WWH ::

Custom Search