Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
computation of trifocal tensor. Aim to get precise result of fundamental matrix is came
true.
(2)
Remove outliers in 3-D point cloud based on the theory of minimum spanning
tree.
(3)
Combined implicit surface fitting method with manifold study method to
complete reestablish of 3-D TIN, taking the characteristics of point cloud into
account, witch is steady, sparse and uneven distributed.
2
Calculation of Fundamental Matrix Based on Three Views
2.1
Three Views Constraint
Three views constraint-the trifocal tensor, has analogous properties to the fundamental
matrix of two view geometry: it is independent of scene structure depending only on the
relations between the views. The view matrices may be retrieved from the trifocal
tensor up to a common projective transformation of 3-space, and the fundamental
matrices for view-pairs may be retrieved uniquely.
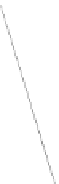
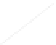
The essence of the epipolar constraint over two views is that rays back-projected
form corresponding matching points are coplanar, a weak geometric constraint, as in
figure 1
X
C
c
e
e
l
l
S
x
c
l
R
c
e
e
R
R
x
R
c
l
x
c
l
R
cc
e
x
l
x
cc
C
cc
C
l
e
l
c
e
e
c
C
C
c
X
Fig. 1.
Epipolar constraint
Fig. 2.
Geometric constraints of Three-View
C
and
C'
are the centers of the two cameras when they are getting the views
R
and
R'
. The camera baseline
C
C'
intersects each image plane at the epipoles
e
and
e'
,
x
and
x'
are the points which imaged by a 3-space point
X
in two views
R
and
R'
. Any plane
π
containing the baseline
C
C'
and point
X
is an epipolar plane, and intersects the
image planes in corresponding epipolar lines
l
and
l'
.
l'
is the epipolar line of point
x
,
and it passes through epipoles
e'
and point
x'
,the corresponding point of
x
in another
image. So, given a pair of image ,it was seen in figure 1, the epipolar geometry
constraint can only guarantee that any point
x'
in the second image matching the point
x
must lie on the epipolar line
l'
. But exact position where the point is could not be
determined. Compared with epipolar geometry, the three views geometry is the ability
to transfer from two views to a third: given a point correspondence over two views the
position of the point in the third view is determined as in figure 2.













































































































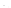

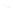
















































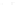
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search