Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
By repeatedly using this principle we can find out multiple camera spatial position
relations between each other.
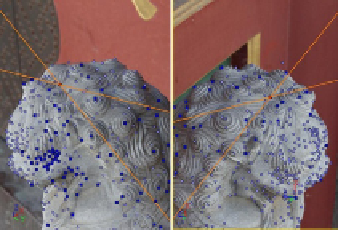
Put some identification points on the reference substance or the sculpture itself in
software called Imagemodeler to complete the calibration of camera [7]. These points
are chosen as space restriction points to compute the camera's spatial position. After-
wards, the same point would be located in different views just as Fig.2 shows, based on
which every assigned feature point in photos can be located in three-dimensional space.
Fig. 2.
Determine space position of feature points by two views
Because of the complexity of stone lion's shape, thousands of feature points are
needed to describe its curved surfaces. After identifying all the feature points, triangu-
lar meshes can be built by linking all these points according to the topological rela-
tionship between them. After mapping the texture information from color photos onto
3D mesh surfaces, a model of stone lion is finished as showed in Fig.3.
Fig. 3.
Left: Stone lion's surface mesh based on feature points Right: Surface model with tex-
ture
3.3
Multi-view Stereopsis Algorithm Based on Photos
The 3D reconstruction based on feature points above can obtain complex-shaped
models, while in the process of feature points selecting a large amount of human inte-
raction is needed rather than totally automation. As for those artifacts carved in relief
with a simple integral shape and complex detail expression, the two approaches talked
above cannot generate realistic and accurate models. Furukawa et al. [8] have pro-
posed an algorithm for multi-view stereopsis that outputs a dense set of small rectan-
gular patches covering the surfaces visible in the images (PMVS). This algorithm has


Search WWH ::

Custom Search