Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
These images can also be divided into 3 categories according to the angle between the
image plane and the chess-board plane: high position (the angle is less than 30 degree),
middle position (the angle is less than 60 degree and more than 30 degree), low position
(the angle is more than 60 degree). As
stated
before, the camera focuses mainly on the
objects to be reconstructed, so the
calibration pattern
is often captured with imperfect
focus, which often cause blurriness in the condition of low position. We separately
measure the average distance between the projected points of the 3D vertices and the
vertices detected with Harris, ChEss and our detector. As shown in
Fig. 13
, our detector
performs as well as ChEss, while much better than Harris, the average reprojection error is
less than 1 pixel in all three conditions. We can also see that imperfect focus affects the
accuracy, but our detector performs much more stable than Harris. ChEss is rather accu-
rate but tends to produces much more false features and the sing-scale property also ag-
gravates its limitation.
(a) (b) (c)
Fig. 12.
Three categories divided by camera positions (a) high position (b) middle position
(c) low position
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
low position
middle position
high position
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
/
通用格式
our detector
ChEss
Harris
Fig. 13.
Reprojection error of ChEss, Harris and our detector
Successful chess-board detection is to extract enough vertices, while discarding the
false ones, and map them to 3D locations in the board to complete the camera calibration.
There are generally three kinds of approaches in this field: J. Sun's method using LSC
and line fitting scheme, Escalera method combining Harris with Hough transformation.



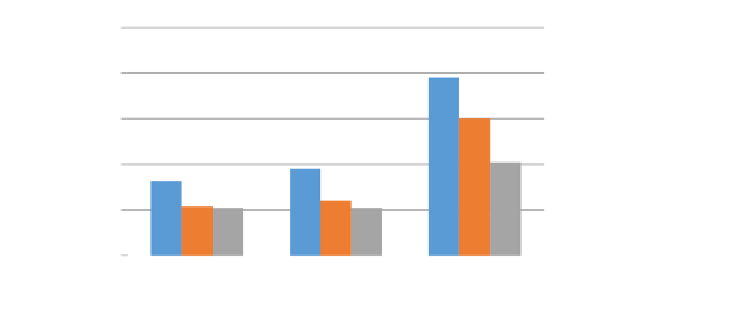





Search WWH ::

Custom Search