Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
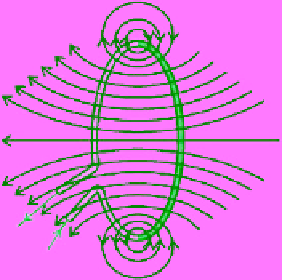
Figure 2.1
Field lines of a
magnetic dipole field. (a) The
classic experiment of iron
filings following the field
lines of a bar magnet (This
figure is in the public domain
in the United States).
(b) Dipole field lines created
by an electric current flowing
in a loop.
Source: http://
N
S
-
+
but can be split apart into separate electric charges (e.g., electrons and posi-
trons), the magnetic poles in a magnetic dipole cannot be separated into
individual magnetic monopoles. This observation makes Maxwell's equations
governing electricity and magnetism asymmetric and has been a source of
puzzlement to physicists, but the practical meaning is that no matter how
much you subdivide magnetic material, it only breaks into smaller and smaller
magnetic dipole moments. It is the fundamental nature of material magne-
tism. A magnetic dipole moment can also be generated by an electric current
(moving electric charges) flowing in a loop (Figure 2.1).
A magnetic dipole moment generates a magnetic field with a characteristic
geometry (Figure 2.2) in which field lines emerge from the N (+) magnetic
pole and loop around to enter into the S (-) magnetic pole. The magnetic
dipole field can be described by the following equations:
M sin
r
3
θ
H
=
(2.1)
θ
2M cos
r
θ
H
=
(2.2)
R
3