Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
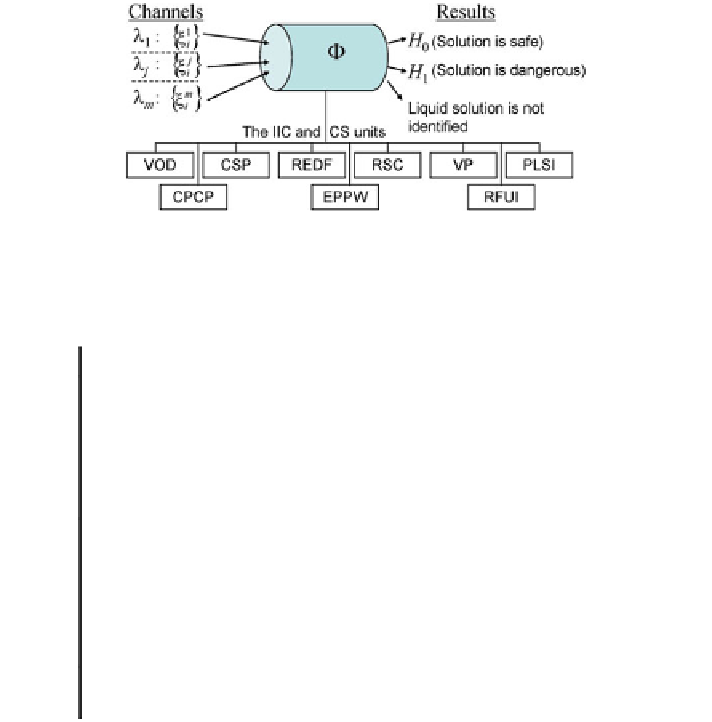
Fig. 10.3 A conceptual block-diagram of the procedure used to identify liquid solutions under the
isolated conditions. Notation is given in Table
10.1
Table 10.1 Description of the IIC and CS as the ESAILS units schematically shown in Fig.
10.3
Unit Characteristic of the unit
VOD Visualization of the observed data (spectra, correlations, statistical parameters,
empirical and theoretical functions of distribution)
CPCP Calculation of parameters for the classical procedure of decision making by using the
Neuman-Pearson criterion
CSP Calculation of statistical parameters and other characteristics, formation of the vector
space {u
i
}
EPPW Estimation of the parameters that will be used in the procedure of the Wald
successive analysis in decision making
REDF
Reconstruction of the empirical distribution functions
Reconstruction of the functions of the user
'
s interface equipped with software to
intervene in the working regime of the expert system at any stage of its functioning
RFUI
RSC
Realization of statistical criterion to estimate the theoretical function of distribution
PLSI
Procedure of the liquid solution identification
VP
Visualization procedures
spectral images of the liquid solutions represented by points in the multi-dimen-
sional vector space of indicators, pre-calculated on the basis of learning samples. In
particular,
identi
cation algorithms (ID) carry out
the task of liquid solution
assessment.
The principal scheme of the CS unit providing the procedure of identi
cation is a
i
j
recorded at the
moment t
i
in the channel
ʻ
j
enters the algorithm
ʦ
, where two hypotheses H
0
and
H
1
are identi
transformation
ʦ
(Fig.
10.3
, Table
10.1
). The light intensity
n
ed. The ESAILS operator determines initial data vi,
i
,
α
and
ʲ
and
decides which parameters u
i
=(u
1
,
…
,u
r
) will be calculated from measurements of
i
j
}. The service unit IIC makes it possible to form vector ui
i
from statistical
characteristics of the series {
{
n
i
j
} or to use direct measurements. The a-priori
information characterizes the type of distribution f
a
(u
i
). The function
n









Search WWH ::

Custom Search