Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
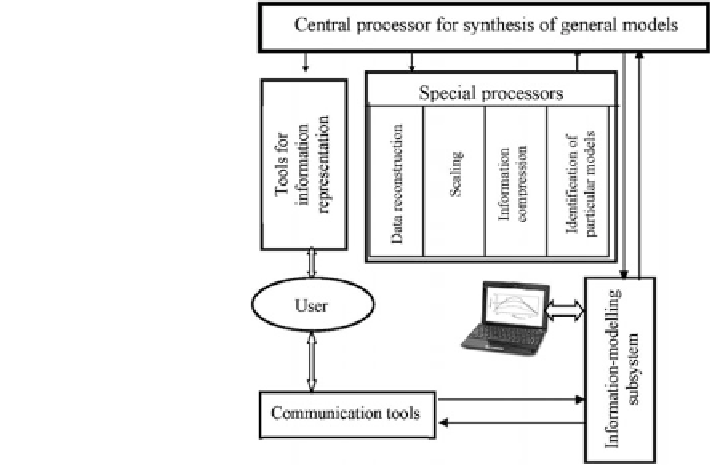
Fig. 1.8 Principal structural
scheme of evolutionary
technology use in the
information-modeling
monitoring system
The GIMS using mainly the item ESA develops models that describe processes
of the air-pollution spread due to different anthropogenic activity. The change in the
concentration of every atmospheric pollutant C is described by the following
equation:
Þ
=
@
t
þr
!
C ¼
r
D
r
C
þ
R
@
Ct
; u; k;
h
ð
ð
1
:
1
Þ
is the wind velocity,
where
!
V
u
;
are latitude and longitude,
respectively; h is the altitude, t is the time, D is the molecular diffusion coef
V
k
;
V
h
ˆ
and
ʻ
cient,
R is the changes due to atmospheric turbulence, emission and mixing.
The item ESA refers to model of Gauss-type as an essential procedure for the
dispersion of the atmospheric pollutants. This model requires a preliminary input
information about the height of pollution source and dispersion characteristics
within the pollutant cloud. The different approximations of the Gauss stream in the
neighborhood of the pollutant sources depend on the stability parameters of the
atmospheric surface layer. The model con
guration depends on geographical
coordinates. For example, clusters with stable and unstable air-pollutant
uxes are
considered primarily within the boundaries between the areas land and water. With
this approach, three speci
fl
c zones can be selected: the zone with undisturbed
dispersion,
the precipitation zone and the delay zone. Each zone has speci
c
equations for the parameterization of the air-pollution dispersion.
In the zone with undisturbed dispersion, the pattern of distribution of the air-
pollutants
fl
fluxes is in
fl
uenced by an homogeneous and stable layer, i.e.,:
Search WWH ::

Custom Search