Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5.22 Basic components of ESPAP functioning
Table 5.20 Components of the ESPAP database
Element of A
2
identifier
Rate of dry deposition (cm s
−
1
)
SO
2
NO
2
Water surface
0.2
1.5
0.01
0.04
-
-
Lime surface
0.3
-
1.0
0.03
-
0.1
Acid dry soil
0.1
0.5
0.01
0.05
-
-
Acid wet soil
0.1
0.8
0.01
0.08
-
-
Plants <10 cm
0.1
-
0.8
0.02
-
0.25
Plants from 10 cm to 1 m
0.2
1.5
0.4
0.7
-
-
Forest
0.2
2.0
0.1
0.8
-
-
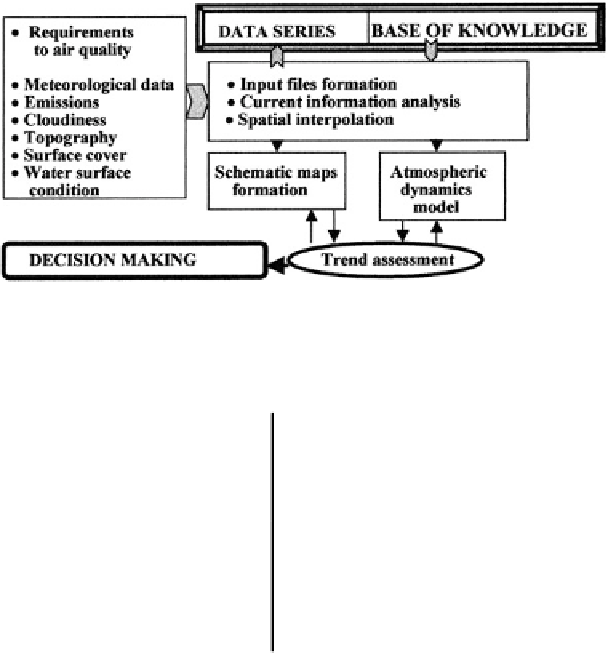
5.8.4 A Subsystem for Control and Visualization
The ESPAP provides a wide hierarchical dialogue for the user with the computer
version of the simulation system of aerosol propagation in the atmosphere. An
adaptation to the territory in the regime of dialogue is accomplished at the expense
of identi
ers which ensure the formation of database fragments responsible for the
structure of surface covers, meteorological situation, and environmental parameters
including information about the sources of aerosols and their characteristics. The
operator
is interaction is shown schematically in Fig.
5.23
.
The ESPAP operates with schematic maps containing conditional images of the
Earth surface or distributions of the atmospheric parameters. The schematic pre-
sentation of the modeling results is connected with their transformation into one of
the following forms of distribution of the parameter to be estimated:
'
schematic representation (1-D, 2-D, 3-D);
symbolic representation of a 2-D image;
tabulated representation by a set of formats;











Search WWH ::

Custom Search