Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
sð
f
;
z
m
Þ
¼2
Z
H
z
Þð
R
þ
z
Þ
dz
ð
R
þ
z
Þ
cð
t
;
q
;
2
2
ð
R
þ
z
m
Þ
z
m
where
cient, f is the sensing frequency, z is the height,
z
m
is the minimal distance of trace from Earth
ʳ
is the gas absorption coef
is radius, H is
the height of satellites orbits. A possibility of passive sensing of ClO, for instance,
is de
'
is surface, R is the Earth
'
ned by the expression for the limb brightness temperature:
z
m
Þ
¼2
Z
H
z
Þð
R
þ
z
Þ
ð
R
þ
z
Þ
T
ð
z
Þcð
f
;
q
T
j
ð
f
;
Q
1
ð
z
Þþ
Q
2
ð
z
Þ
½
dz
;
2
2
ð
R
þ
z
m
Þ
z
m
where
0
1
Z
H
n
ð
R
þ nÞ
cð
f
; nÞð
R
þ nÞ
d
@
A;
Q
1
ð
z
Þ
¼0
:
5exp
q
2
2
ð
R
þ
z
m
Þ
z
0
1
Z
H
n
ð
R
þ nÞ
cð
f
; nÞ
d
@
A
Q
2
ð
z
Þ
¼0
:
5exp
sð
f
;
z
m
Þþ
q
2
2
ð
R
þ
z
m
Þ
z
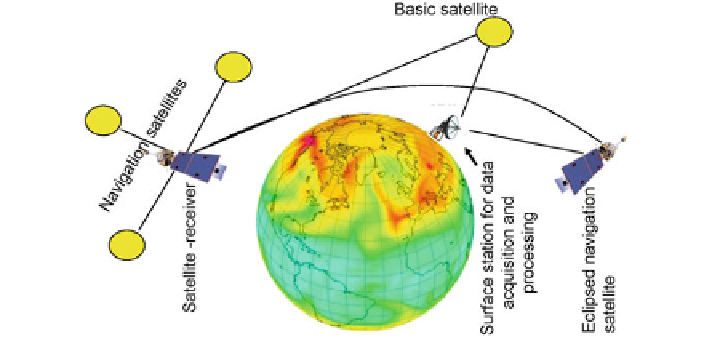
The radio-trauslusense method with using two satellites at frequencies of strong
gas absorption lines proves to be effective approach to the ozone layer characteristic
measuring (Strelkov 1995; Yakovlev 2001; Yakovlev et al. 2009). Enhancement of
this method is given by Yakovlev et al. (2009). Radio-eclipsing method of the Earth
sensing is proposed. Principal scheme of this method is characterized in Fig.
2.25
.
Fig. 2.25 Schematic diagram of global monitoring system based on the radio translusense method




Search WWH ::

Custom Search