Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Beginning from 1970, in the OECD countries the problem of air quality has
become the subject of studies at many scienti
c centers. Oil from the counties of the
Middle East becomes the main source of energy. The content of sulfur in oil
constitutes 2.5
3 %. In 1985 some European countries signed the CLRTAP pro-
tocol on a 30 % reduction of sulfur emissions. As a result, now SO
2
emissions
decreased by more than 50 % compared to 1980. Of course, this was possible
largely due to transition of Europe to the use of Russian gas.
It should be mentioned that along with the formation of acid rains, sulfur
compounds directly affect a decrease of the greenhouse effect. For instance, sulfate
ion has an opposite effect on a change of air temperature compared to CO
2
and,
hence, reduces the effect of climate warming. Photochemistry of sulfur cycle has
two the most important reactions:
-
reaction from source gases to SO
2
, and
reactions leading from SO
2
to H
2
SO
4
.
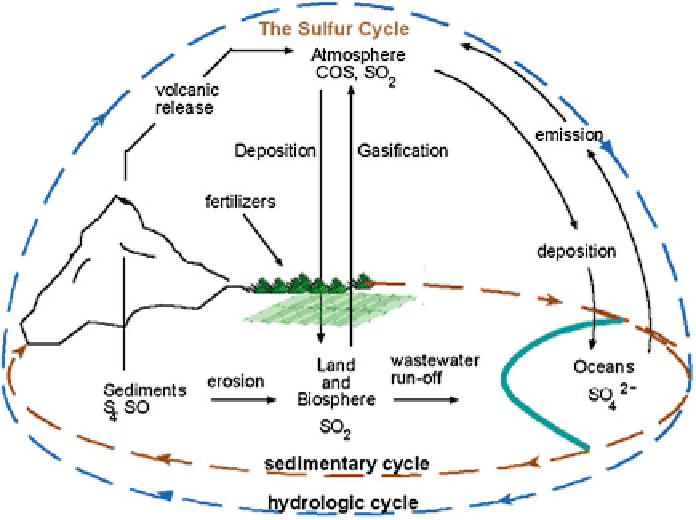
The global sulfur cycle consists of the mosaic structure of local
fluxes of its
compounds with other elements formed due to water migration and atmospheric
processes. It is schematically shown in Figs.
1.42
and
1.43
. The conceptual schemes
of the global and regional cycles of sulfur have been described in detail by many
authors (Nitu et al. 2000b; Krapivin and Varotsos 2008). However, the existing
fl
Fig. 1.42 Principal scheme of global sulfur cycle (
http://www.enviroliteracy.org
)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search