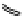Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 11-3.
A cluster implemented with a replica set
Replica sets also feature the concept of
active
and
passive
members. Passive secondary servers don't
participate in elections for a new primary when the current primary becomes unavailable; instead, they serve the
same purpose as
hidden
members
,
and they can be used as reporting or backup datasets.
Member servers of replica sets do not need to be designated as set members on startup. Instead, configuration is
done through server-level commands that are sent through the normal server interface. This makes it easier to create
configuration management tools that allow dynamic configuration and management of clusters of machines.
In the upcoming sections, you will learn how to accomplish the following:
1.
Create a replica set.
2.
Add a server to a replica set.
3.
Add an arbiter to a replica set.
4.
Inspect and perform operations on a replica set.
5.
Configure individual members of a replica set.
6.
Connect to a replica set from your application.
7.
Set Read Preference from within your application
8.
Set Write Concern from within your application
9.
Use Replica Set tags with Read Preference and Write Concern
10.
Use the web interface to inspect the status of your replica set