Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Applied force
Applied force
spherical indenter
spherical indenter
Rings
Rings
Membrane
Membrane
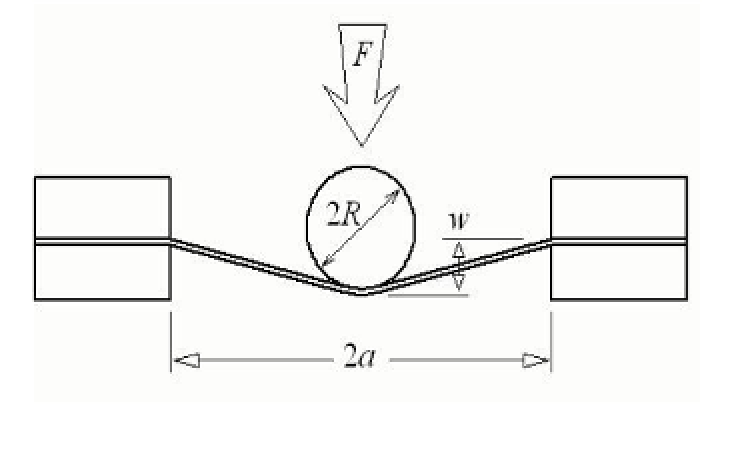
Figure 10-3. Schematic of experimental setup of shaft-loaded blister test.
tensile force on the film in the radial and circumferential directions. The
bending-stretching range can be used to characterize from multi-cell up
to tissue level. Extreme loading leads to large deformation governed by
rubber elasticity.
It is worthwhile to note that the new indentation method for
freestanding membrane, though similar, is significantly different from
conventional nanoindentation. Either configuration requires the applied
load to be in the sub-mN range, but the former might require
the shaft displacement to be in the millimeter range depending on the
membrane radius and thickness. The large actuation displacement re-
quirement might exceed the maximum extent that most nanoindentation
systems can handle, which is less than 1 mm.
Besides the capability of measuring materials properties in a typical
loading-unloading cycle, the new method is useful for fixed-load
measurements,
e.g.
creep test.
14
A ball bearing of fixed weight can be
dropped onto the film center, thus allowing the load to be unchanged in
either a dry or aqueous environment for a prolonged duration in terms of
and mechanical drift as in all force sensing devices. This is by far the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search