Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 9-6.
Comparison of a quasi-static indent (dashed line) and a force curve (solid
line) in the same sample, a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sample with a nominal elastic
modulus of 3 MPa. Comparison of maximum displacements for the two types of indents
reveals the large error in displacement calculation (and hence contact area calculation)
that results from analyzing only the quasi-static indent and losing the information
contained in the full force curve.
contact but tensile loading near the edges. When indenting anisotropic
materials, it has been demonstrated that the indentation modulus
represents a weighted average of moduli along the principal axes of the
material, dominated by the modulus in the orientation of indentation.
93
Hence, anisotropic moduli measured by indentation are influenced by
the moduli in the other orientations, and are not as different from
one another as anisotropic moduli measured through uniaxial testing
techniques. Vlassik and Nix
93
presented a method for calculating
anisotropic moduli from indentation moduli in anisotropic materials, and
this has been applied to measurements in bone samples.
94-96
Although many soft tissues, such as cartilage, also exhibit structural
anisotropy down to small length scales, rigorous anisotropic indentation
analysis has not been applied to other biological materials due to the
complexity of the current models. Moduli in multiple orientations have
been measured in numerous biological materials using nanoindentation,




















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































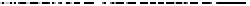





































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search