Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1000
800
600
5
400
Indenter:(60
o
, 63.14
o
, 70.3
o
, 75
o
, 75.79
o
, 80
o
)
α =
200
75.79
o
80
o
4
0
75
o
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
Uniaxial strain,
ε
3
(a)
70.3
o
2
63.14
o
60
o
1
0
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
Indentation depth,
δ
(
μ
m)
1500
1500
mat7
1000
1000
ma t1
250
500
500
α
=
80.0
o
200
0
0
0
0
0.05
0.05
0.1
0.1
0.15
0.15
Uniaxial strain, ε
Uniaxial strain, ε
150
75.8
o
100
(b)
70.3
o
50
63.1
o
0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Indentation depth, δ (nm)
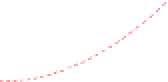
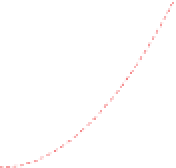
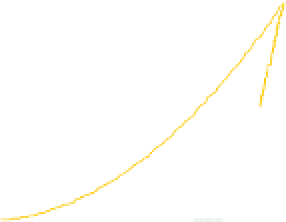
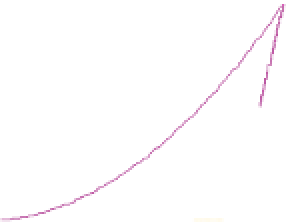
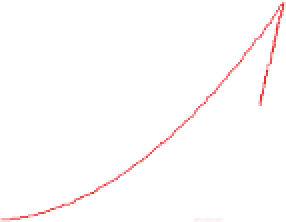
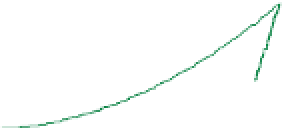
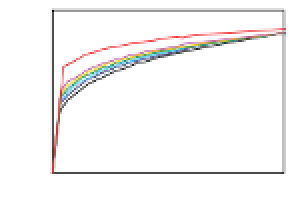
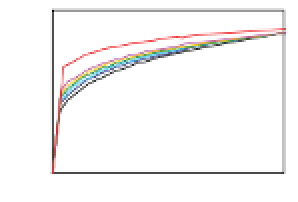
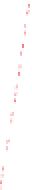
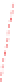
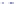
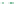
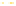
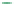
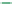
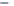
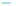
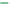
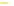
Figure 6-7. Examples of mystical materials; the
P
−
h
curves of mystical materials and
the uniaxial
curves of mystical materials are given in insert on the top-left corner.
(a) The Poisson's ratio is fixed at 0.3. A pair of mystical materials with
E
1
= 100
GPa
,
σ
y
1
= 872.47
MPa
,
n
1
= 0.0 (solid curve) and
E
2
= 103.75
GPa
,
σ
−
ε
σ
y
2
= 715.61
MPa
,
n
2
=
0.10663 (dash curve). They cannot be distinguished by indenter angles from 60° to80°.
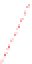
(b) The Poisson's ratio is allowed to vary (from 0.499 to 0.0 for mat1 to mat7). The
material properties (
E
(
GPa
),
σ
y
(
MPa
),
n
) are (104.23, 0.499, 574.4, 0.2434), (113.4,
0.40, 627.6, 0.2173), (116.9, 0.35, 659.4, 0.2038), (120.0, 0.30, 691.8, 0.1913), (122.2,
0.25, 725.5, 0.1784), (123.9, 0.20, 762.8, 0.1653), and (127.5, 0.0, 947.2, 0.1047),
respectively, for mat1, mat2, mat3, mat4, mat5, mat6, and mat7.
ν
,









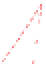

















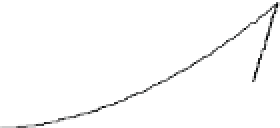


































































































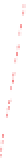






















































































































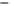










Search WWH ::

Custom Search