Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
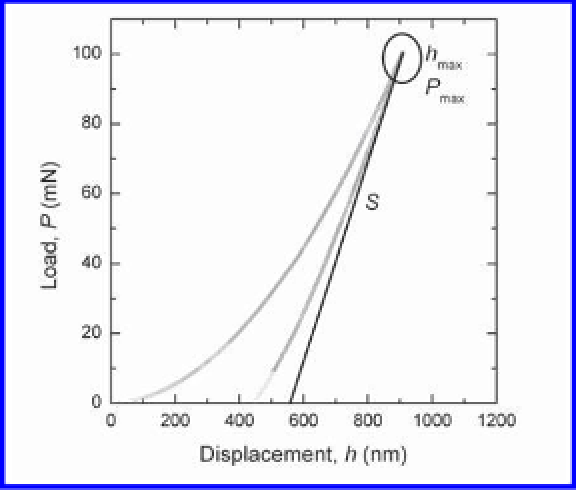
Figure 5-6. Elastic-plastic indentation responses for a Berkovich on fused silica glass,
illustrating the three parameters taken directly from the load-displacement (
P
-
h
) response
for Oliver-Pharr
1
analysis:
h
max
,
P
max
,
S
.
projected area calculated from the contact displacement (
h
c
) via a
for both a four-sided and a three-sided pyramid that the indenter was
infinitely sharp. However, in reality the tip is blunt at small indenter
depths as a pyramid cannot be made perfectly sharp. The probe therefore
approximates a sphere at some small contact depth
h
c
. The hardness is re-
defined as
H
c
=
P
max
/
A
c
(
h
c
) where the relationship between contact depth
and contact area is often taken as a summed polynomial of the form
C
k
h
1/2
(k-1)
A
c
(
h
c
) =
C
0
h
c
2
+
(5-13)
k
=
1
in which the coefficients
C
i
are determined by calibration. Other
functional forms are possible, such as the physically-meaningful
14
:
A
c
(
h
c
) = (π tan
2
ψ )
h
c
2
+ 4
R
π
h
c
+ 4
R
2
π cot
2
ψ
(5-14)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search