Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
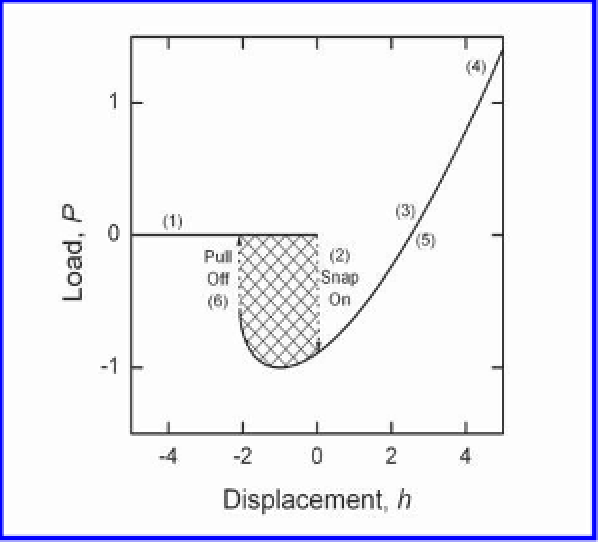
A JKR contact sequence under displacement control is then, with
reference to
Figs. 4-22
and
4-23
,
given by: (1) reversible approach of the
sphere to the surface along the
P
=
0 line with
a
=
0 and
h
<
0 ; (2) at
0 and
subsequent positive infinitesimal perturbation of either
a
or
h
leads to
an irreversible non-equilibrium increase in
a
and decrease in
P
until a
stable equilibrium condition is reached with
a
> 0 and
P
< 0 (the sphere
has snapped-on to the surface). Subsequent infinitesimal increase of
h
leads to reversible quasi-equilibrium increase of
a
through a sequence of
stable equilibria until the quiescent point (3) is reached at
P
= 0. Further increase in
h
leads to increases in
a
and a reversible
adhesive indentation process (
P
> 0) until (4) maximum displacement
and contact radius is reached.
h
=
0 an unstable equilibrium condition is reached at
P
=
Figure 4-22. Variations in the contact load with displacement for a JKR contact cycle
under displacement control. The system is sub-critical, leading to a hysteresis loop in the
h
0
contact cycle that is bounded by “snap-on” and “pull-off” instabilities on approach
and retraction, respectively. The values are normalized using the characteristic values
(Eqs. 4-56
to
4-58).
=
Search WWH ::

Custom Search