Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
variation of
Fig. 4-7
as a function of this distance.
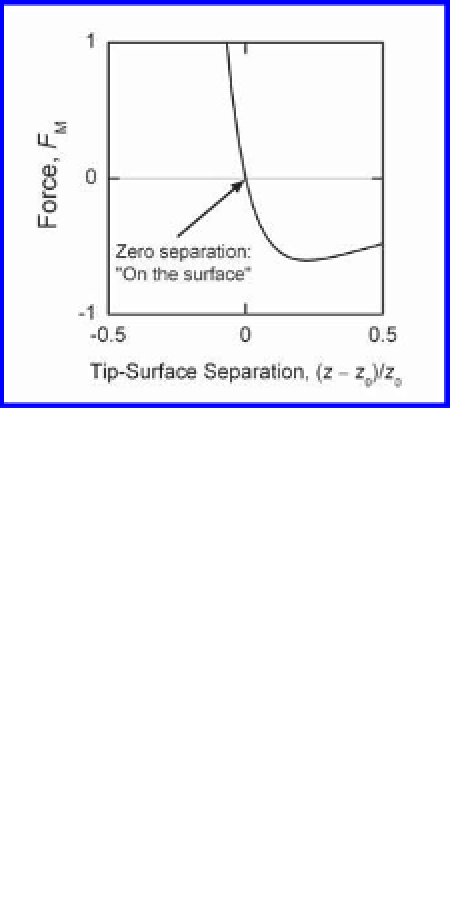
Figure 4.8. An expanded view of the force between a surface and a tip around the
F
M
= 0
separation from this equilibrium position.
Important as the equilibrium configuration
(
z
0
, Φ
0
)
, defined by the
extremum in the potential
Φ
M
, is for setting the boundary between
indentation and separation states, the previous section showed that it is
extrema in the force and stiffness fields that are important for
determining equilibrium and stability behavior. In this case, extrema in
F
M
and
k
M
place bounds on external influences, most importantly the
probe spring, that can give rise to snap-on and pull-off behavior.
Setting
k
M
0
provides the configuration
(
z
1
,
F
1
)
in which the surface
exerts the greatest attraction (numerically minimum force,
F
1
=
0
) on the
<
tip:
1/(
mn
−
)
m
zz
n
+
1
1
(4-24)
=
1
0
+
n
+
1
Φ
mn
z
(4-25)
F
=
0
0
1
zm
+
1
z
0
1

Search WWH ::

Custom Search