Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
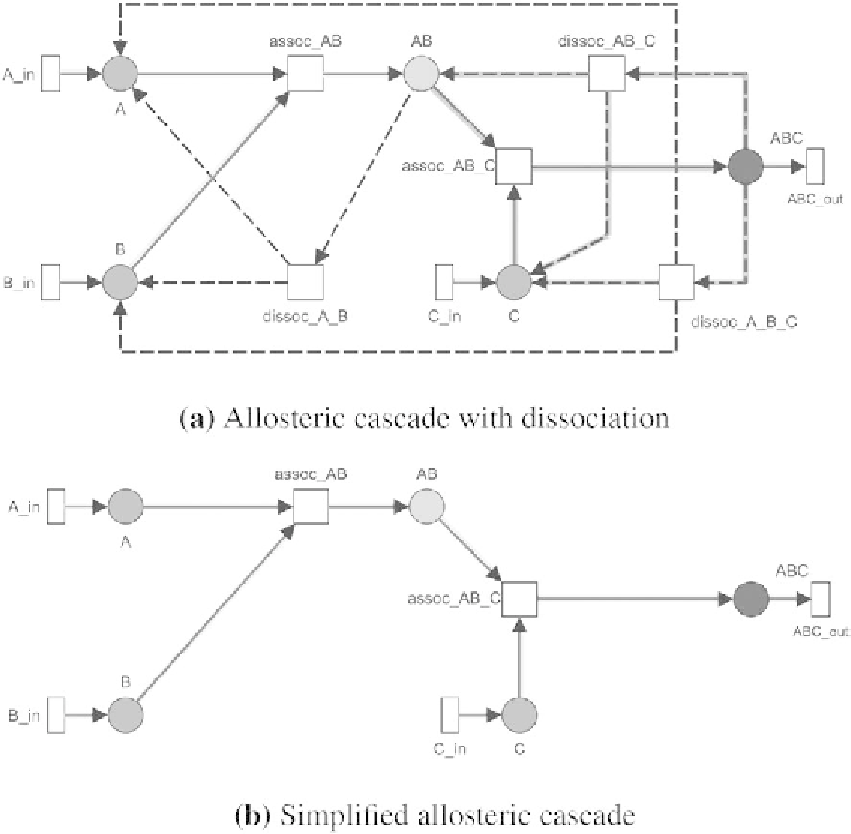
Fig. 3. Example of a module for protein complex association where two molecules
A
and
B
form a heterodimer,
AB
, which
defines a necessary step for binding the factor,
C
, in progressing the complex assembly through complex
ABC
. (a) PN module
with reactions, forming (solid lines) and decomposing (dashed lines) intermediate complexes. Two of four T-invariant pathways,
completely covering this module, are colored, and define the main signaling route (blue) and a cycle (red); green
=
source
factors, gray
=
intermediate factors (complexes); blue
=
target complex; (b) The same model without dissociation reactions
strongly reduces structural complexity, leading to one T-invariant. (Colours are visible in the online version of the article at
minimal T-invariants, reflecting the important aspects of functional
ABC
and non-functional
IAB
formation. The simplified version may suffice in many cases, in particular when time points of
protein activities are unknown, for example, the time when a specific factor dissociates from an
intermediate complex. This net module is easily derived from the basic allosteric cascade shown
in Fig. 3b) by adding the node I and introducing an additional edge that purges
AB
.