Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
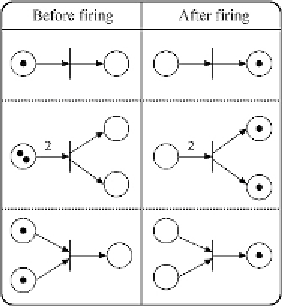
Fig. 3. Examples showing firing rules of Petri nets.
Fig. 4. Lower two output transitions are in conflict. The place whose output transitions are in conflict is called a
conflict place
.
A place can hold a positive integer that represents the number of tokens. An assignment of tokens in
places expressed in form of a vector is called
marking
M
, which varies during execution of a Petri net.
Firing rule of Petri net
PN
: A transition
t
is firable if each input place
p
I
of
PN
has at least
α
e
(
e
=
(
p
I
,
t
)) tokens, where
α
e
denotes the weight of an arc
e
=
(
p
I
,
t
). Firing of a transition
t
removes
α
e
tokens from each input place
p
I
of
t
and deposits
β
e
(
e
=
(
t
,
p
0
)) tokens to each output place
p
O
of
t
.
Figure 3 shows the movement of tokens by the firing of the transition.
Conflict-free Petri net
A
conflict
(see Fig. 4) corresponds to the condition of a place that has at least two output transitions
and has an insufficient number of tokens for firing. Deterministic resolutions are considered to decide
the firings of the transitions. Usually, the concepts of priority-order and probability are employed when
dealing with timed Petri nets, stochastic Petri nets and high-level Petri nets [11,12]. A Petri net is called
a
conflict-free Petri net
if no such conflict exists, which is a subclass of Petri nets.
Timed Petri net
Petri net can be extended by assigning a delay time of firing to each transition for facilitating a
system-level understanding by means of simulation. Such an extended Petri net is called a
timed Petri
net
.