Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
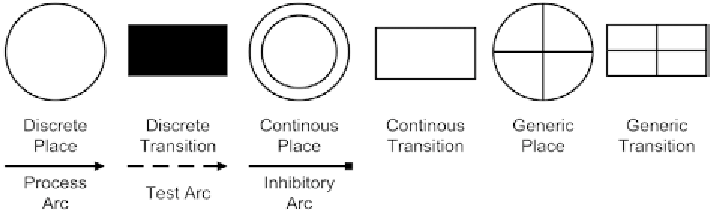
Fig. 4. This figure shows the fundamental symbols of HFPN [Matsuno
et al.
, 2003]*.
P
N
represents any number
IN
or the number of tokens represented by the place
P
N
regarding the
actual configuration of
FPN
. The advantage of the
FPN
is that kinetic effects of biological networks
can be simulated. Therefore, any qualitative Petri net model of a biological network can be extended
by using the functional Petri net and including quantitative experimental data (for example quantitative
proteomic data or kinetic data of enzymes).
Regarding molecular biology we can see an exponentially growing amount of quantitative data.
Therefore, any more realistic simulation of biological networks required more extensions. The usage
of real numbers instead of tokens is one important aspect of the Hybrid Functional Petri Net (HFPN)
[Matsuno
et al.
, 2003]. The HFPN is an extension of the Hybrid Petri Net (HPN) [Alla and David, 1998].
The idea of the HPN was the representation of two kinds of places and transitions that allow calculating
the discrete and analytical molecular values. Therefore, discrete places (discrete transitions) and the
continuous places (continuous transitions) were defined (Fig. 4). The idea of the continuous place is that
nonnegative real numbers can be used, which can be interpreted as the concentration of metabolites.
METHODS
Due to the complexity of pathway interactions and large number of components involved in signal
transduction, cellular rhythms and cell-to-cell communication, it is quite difficult to intuitively understand
the behavior of cellular networks. Still, we do not understand many fundamental laws of biology.
Laboratory experiments for testing hypotheses are in terms of cost, ease and speed quite expensive.
Computer modeling and simulation techniques have proved useful for testing hypotheses
in silico
.
Experiments that are infeasible
in vivo
, such as gene knock-outs of vital genes, can be performed
in
silico
. Dynamic computer models are able to monitor cellular rhythm, signal transduction, cellular
metabolism, changes and influences within a system. Furthermore, computer based models can suggest
novel experiments.
Besides the traditional modeling and simulation approach based on ordinary differential equations
(ODEs), partial differential equations (PDEs) and stochastic differential equations, the approach of using
Petri nets and logic based descriptions are widely used to analyze biochemical networks [Gilbert
et al.
,
2006].
The advantage of Petri nets is the structural analysis and temporal logic.
Petri nets perform
sophisticated model analysis and relate predicted behavior and observations.
*A colored version of the figure/chart is available at
In Silico Biol.
10
, 0003 <
http://www.bioinfo.de/isb/2010/10/0003/
>
, 1
February 2010.