Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
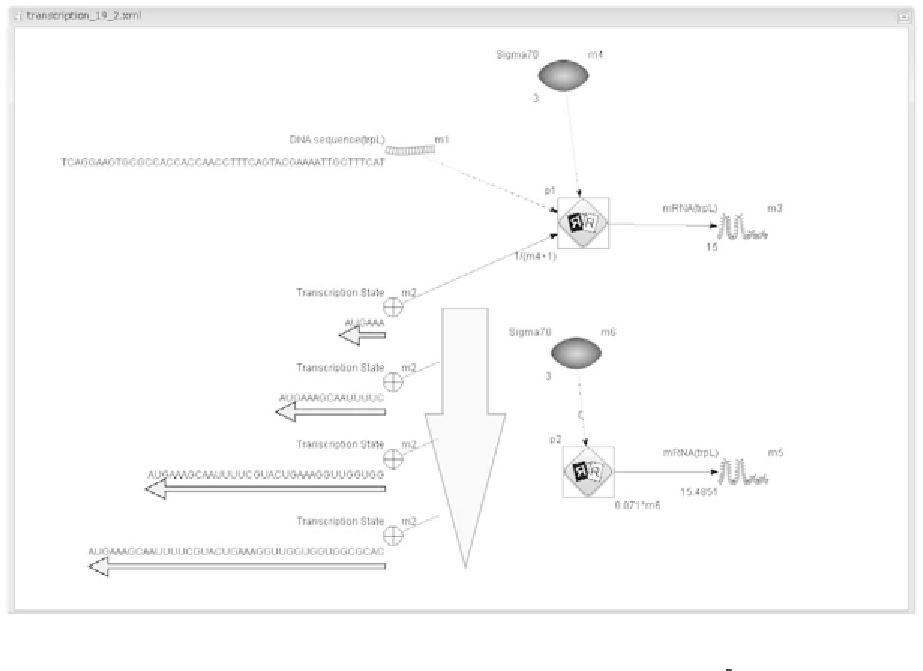
Fig. 2. Transcription simulation of sequence level on Cell Illustrator. The upper part shows a sequence level simulation model
using generic entities and a generic process (
http://www.csml.org/download/model/csml30/generic transcription 30.xml
)
. In
the lower part, a concentration level simulation model is displayed that uses only one continuous entity and process.
METHODS
Automatic graph layout
When the total number of elements in a biopathway model is fewer than fifty, the function of the
automatic pathway layout is less important. In that situation, it was enough to put and arrange those
elements manually. No automatic layout function was implemented in Cell Illustrator 1.0 released in
2002. Along with the progress of Systems Biology, there has arisen a strong requirement for handling
larger pathway models and pathway models written in other XML formats that lack graphical layout
information. Naturally automatic layout functionality was keenly demanded to solve this requirement.
The first simple solution was to use a known graph layout library. The later Cell Illustrator has selected
one of the graph layout libraries named JGraph with Circle, Moen, Sugiyama, and organic layout
algorithms [24]. Unfortunately, these layout algorithms were not enough for most biopathway models.
From this fact, new grid-based layout algorithms have been developed [4-6] and implemented in Cell
Illustrator. Figure 3 shows all of the graph layout algorithms, including BLK [4,25], SCCB [6], and Grid
Eades [5]. These grid layout algorithms position the elements on the grid points. With this function,
Cell Illustrator succeeded in laying out the pathway models by considering cellular location information
that has a complicated structure,
e.g.
, a need to position some elements on the internal region of the torus