Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Computational Intelligence
Neural Networks
Evolutionary
Algorithms
self organizing networks
backpropagation
spiking networks
classification
representation
optimization
self-adaptation
evolution strategies
genetic algorithms
genetic programming
Reinforcement
Learning
value iteration
q-Learning
learning behavior
optimization
Memetic Algorithms
evolution and local search
information sharing and
communication
information sharing
optimization
control
inference
optimization
emergent
behavior
Artificial Immune
Systems
pattern recognition
hypermutation
Fuzzy Logic
fuzzy rule bases & inference
fuzzy representation
and modelling
Swarm Intelligence
particle swarm optimization
ant colony optimization
flocking
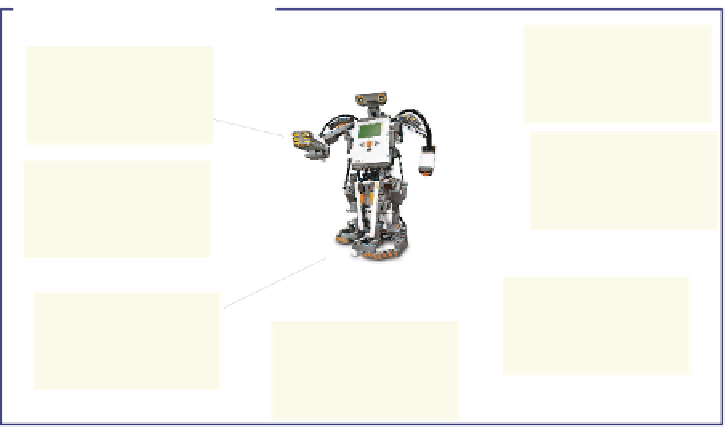
Fig. 2.1.
Survey of the techniques of CI; photo with permission of LEGO Group
intended to construct more than a single-processor system, but dreamt of in-
telligent machines even with the possibility of self-reproduction. In the history
of AI many approaches were proposed to achieve this objective. Most methods
can be classified into two classes: symbolic and subsymbolic approaches. The
latter one is also called
computational intelligence
(CI),
soft computing
or
natu-
ral computation
. CI comprises neural networks, fuzzy-logic and EAs. Meanwhile,
also swarm intelligence, memetic algorithms, artificial immune systems and re-
inforcement learning can be ranked among CI. These methods also have the
feature in common that they are biologically inspired approaches. Figure 2.1
gives an overview of the CI fields.
The field of EC comprises biologically inspired optimization methods and is
subject to the work at hand. Memetic algorithms combine evolution with local
search. Fuzzy logic enables the representation and modeling of linguistic terms
and the inference with rule bases. The field of swarm intelligence comprises a
class of algorithms which is inspired by the emergent intelligence of natural
swarms. The most successful methods from this class are particle swarm and
ant colony optimization. Artificial immune systems are optimization heuristics
inspired by processes of the vertebrate immune system like hypermutation and
clonal selection. Reinforcement learning algorithms comprise a class of algo-
rithms for the control of agents in dynamical environments. Depending on the
available information value iteration or Q-learning are the mostly used variants.
Neural networks are inspired by natural neural systems like the human brain.
Artificial neural networks are massively parallel systems of neural models, which
are able to solve classification problems. Supervised learning methods exist like

Search WWH ::

Custom Search