Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
process, where intensive interactions between a content problem space and a rhetor-
ical problem space lead to knowledge transformation (Bereiter & Scardamalia,
1987). Finally, we note the constructionist approach of
learning through design
(e.g., Kafai & Resnick, 1996), which has been applied in pedagogy and approved
by many case studies ranging from K-12 education to university and adult educa-
tion levels. Particularly, multimedia design problems using the services of emerging
computer technologies for the support of active learning and media skills acquisition
have become popular. Examples include contextualized multimedia design in ele-
mentary biology (e.g., Beichner, 1994), software design in mathematics (e.g., Harel,
1990; Kafai, 1996), hypermedia design in history and the humanities (e.g., Carver
et al., 1992; Bereiter, 2002; Stahl & Bromme, 2004), and designing instruction in
simulations in physics (Vreman-te Olde, 2006). These examples all involve gener-
ative activities of (a) integrating various media and (b) structuring information for
others. In this context, Erickson, Lehrer, and colleagues (Erickson & Lehrer, 1998;
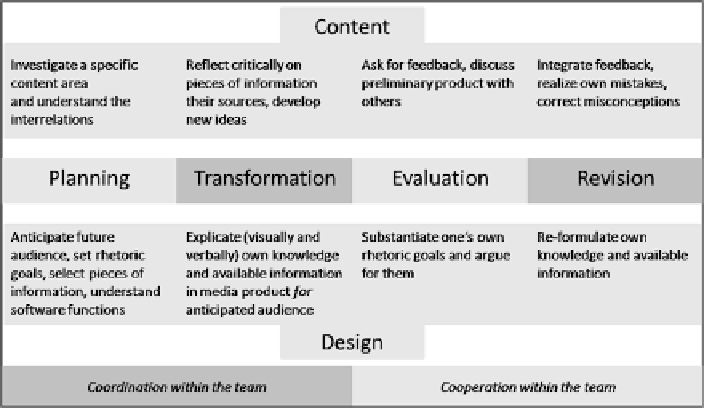
Lehrer, Erickson, & Connel, 1994) emphasized the importance of sub-processes in
design problem solving, such as planning, transformation, evaluation, and revision
in hypertext design for history learning (see Fig. 25.3).
Fig. 25.3
Visual design as problem solving: cognitive and socio-cognitive processes during learn-
ing by designing, accentuating aspects of content, design, and teamwork (see also Zahn, 2009)
These cognitive perspectives are adopted in our works on learning by hyper-
video authoring and creating digital video (Stahl et al., 2005; Zahn et al., 2005).
We assume that students who design digital (hyper)videos, simultaneously have to
take into account both visual content and style of their design product. Thereby
they have to establish a joint dual problem space (for
joint problem spaces
,
see Roschelle & Teasley, 1995) being distributed over the cognitive systems