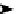Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
�
�
�
�
�
�
�����
����
�
�
�
�
�
�
����
Figure 4.2
The enlargement of river meanders until the river short cuts the
meanders creating an oxbow lake. E is a zone of net erosion and D
is a zone of net sediment deposition.
as braided, meandering and straight channels and a single river may
have each of these patterns in different sections. Braided channels
consist of lots of individual smaller channels which separate and
come together with the islands in between known as bars. The
channels can rapidly move locations with bars eroding on one side
and growing on the other. Braided rivers are common where there
is a lot of mobile sediment such as downstream of a glacier. Mean-
dering channels have a wavy planform. Often waviness is measured
by sinuosity to determine the nature of the measuring channel
where sinuosity is the ratio of the length of river between two
points compared to the length of the straight line valley between
these two points. Straight channels are defined as having a sinuosity
of less than 1.5. A meandering channel refers to a single channel
with a number of bends which result in a channel sinuosity of 1.5
or greater. Straight rivers are more controlled by human action and
natural straight rivers are often unstable and become meandering.
Even a drop of water running down the surface of a perfectly
smooth piece of glass will take a meandering course.
Channel slope and discharge are important controlling variables
on the planform of river channels. For a given discharge there is
often a critical slope above which channels will meander and then