Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
V
CC
V
CC
i
s3
R
s1
P
3
X
3
V
A
Y
3
CCCII
I
s1
i
s1
R
c2
Z
3
Q
3
P
1
X
1
V
CC
I
out
R
L
Y
1
CCCII
R
c1
+
Z
1
Q
1
V
EE
V
in
X
4
P
4
I
s3
−
CCCII
Y
4
V
B
Z
4
Q
4
R
s3
V
EE
V
EE
Fig. 9.45 Frequency doubler proposed in [
44
]
Frequency doubler is widely used in analog signal processing, communication
and instrumentation systems. Frequency doubler is often made from analog multi-
pliers. However, Anuntahirunrat et al. [
44
] have demonstrated that by imposing
appropriate design conditions, the CCCIIs based circuit shown in Fig.
9.45
can
accomplish both these functions from the same structure.
It has been found [
45
] that an approximate expression for the output current of
this circuit is given by:
i
out
k
5
ð
I
DC
þ
I
2
ˉ
cos 2
ˉ
t
Þ
ð
9
:
61
Þ
1
R
C
2
þ
k
5
¼
k
4
V
CC
ð
V
EE
Þ
5
I
1
k
4
R
S
;
k
4
¼
ð
9
:
62
Þ
2
R
x
I
m
2
IðÞ
1
4
k
3
I
DC
4
I
1
k
4
R
S
1
þ
I
2
ˉ
I
1
R
s
K
3
K
4
;
K
3
¼
ð
9
:
63
Þ
;
2
From the above equations, it is clear that by appropriately selecting component
values and parameters, the circuit can generate a cosine wave of frequency two
ˉ
from an input current i
x1
¼
t
derived from the input V
m
.
Siripruchyanun and Jaikla demonstrated in [
45
] that three CCCIIs are enough to
realize a current mode precision full wave rectifier with a couple of advantageous
features. Their preposition is shown in Fig.
9.46
.
The analysis of this circuit can be carried out by noting the following:
I
m
sin
ˉ
I
con
V
T
4
I
B
1
;
v
y
2
2
I
B
2
v
y
3
2
I
B
3
V
T
V
y
2
¼
V
y
3
¼
V
x
1
¼
R
x
1
i
x
1
¼
i
z
2
¼
i
z
3
¼
ð
9
:
64
Þ
V
T
;




































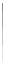

























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search