Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
9.14 CCCII-Based Precision Rectifiers
Full wave precision rectifiers have been proposed in literature using a variety of
building blocks such as op-amps, current conveyors and current feedback op-amps.
A circuit to realize a precision rectifier using CCCIIs was presented in [
43
] which
employ a pair of complimentary MOS transistors and two resistors in addition. This
circuit is shown in Fig.
9.44
.
The lower CCCII provides a current output proportional to the input voltage.
This creates a controlled voltage at the gates of the two MOSFETs in conjunction
with the resistor R which is so selected that both the transistors remain in saturation
even for small input signals. Depending upon whether V
in
is positive or negative,
the gate voltage V
G
would be either +V or -V (this requires that the ratio R/R
x1
is
large which can be achieved by proper choice of I
B1
and R). Here
V denotes the
DC biasing supply voltage of the CCCIIs. An analysis of this circuit shows:
For
2
I
B
2
R
L
V
T
V
in
>
0,
V
G
¼
þ
V
,
V
o
¼
V
in
ð
9
:
59
Þ
and for
2
I
B
2
R
L
V
T
V
in
<
0
V
G
¼
V
,
V
o
¼
V
in
ð
9
:
60
Þ
:
An important merit of this circuit is that the output amplitude of this rectifier is
electronically controllable by external bias current I
B2
.
I
B2
M
n
Z+
V
in
Y
V
0
Z−
X
R
L
M
p
I
B1
Y
Z+
2
X
R











































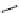





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search