Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
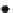
Fig. 8.15 Squaring circuit
proposed by Liu [
8
]
M
3
I
x
V
1
X
V
out
CCII+
Y
Z
I
0
V
G
R
2
−V
1
M
4
To ensure the operation of the circuit as predicted by the analysis, the following
condition should be satisfied:
V
G
>
Vjjþ
V
TH
ð
8
:
22
Þ
Thus, the circuit of Fig.
8.14
functions as a square-rooting circuit.
If complementary inputs are easily available and can be applied then the circuit
of Fig.
8.15
performs the operation of squaring. The output current of this squaring
circuit, assuming the same aspect ratios of the two MOSFETs, is given by:
I
0
¼
ʼ
s
C
ox
W
3
L
3
V
1
ð
8
:
23
Þ
The basic schematic of the squaring circuit can be generalized by adding more input
variables along with additional the modified expression of the output current as
pairs of matched MOSFETs thereby leading to
V
1
þ
I
0
¼
ʼ
s
C
ox
W
V
2
þ ::::: þ
V
n
ð
:
Þ
8
24
L
Finally, if the circuit is further modified as shown in Fig.
8.16
it performs the
function of vector summation for which the relation between the output voltage and
the various input signals is found to be
R
2
R
1
V
1
þ
V
2
þ
...
þ
V
n
V
0
¼
ð
8
:
25
Þ
The workability of the above mentioned circuits has been confirmed [
8
] by realizing
CCII+ using AD844, the unity gain inverting amplifier using LF356 and the
MOSFETs from the CMOS transistor arrays CD40007. The bandwidth of a two
input vector summation circuit has been found to be around 400 KHz.




















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search