Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
R
R
+ −
R
R
+
−
+
R
3
R
4
R
+
C
0
R
R
R
1
C
2
−
−
+
R
5
R
R
−
Z
in
Z
in
c
R
R
R
R
−
+
−
+
R
R
1
2
+
+
R
L
eq
= C
0
R
2
−
V
1
C
0
R
+
V
2
R
1
2
R
−
−
d
−
+
R
3
R
4
1
R
1
C
2
−
+
R
5
−
+
R
1
C
2
L
eq
2
R
3
R
4
2
+
−
1
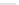
Fig. 5.18 Some inductance simulation networks employing IC op-amps (a) Gyrator-based loss-
less GI, Z
in
¼ sC
0
R
2
s
1
] GIC-based grounded inductance simulator,
Z
in
¼ sC
2
R
1
R
3
R
5
/R
4
(c) Three-op-amp lossless FI due to Glover, Z
1-2
¼ sC
0
R
2
[
6
](d) Two-
GIC-based FI simulator, Z
1-2
¼ sC
2
R
1
R
3
R
5
/R
4
(e) Dutta Roy [
2
] and Wise [
3
] method of FI
simulation using unity gain amplifiers, Z(s)
¼
2(R
1
+R
2
) + 2sC
1
R
1
R
2
(f) A lossy tunable
parallel-RL type floating inductance simulator derived from lossless FI of Sudo and Teramoto
[
8
](g) A lossless FI from
The
and
Yanagisawa
[
1
] b) Antoniou
'
'
s
proposition [
7
] with R
6
¼
R
7
¼
R
8
¼
R;
R
1
¼
R
2
¼
R
4
¼
2R; R
3
¼
2R/3; R
5
¼
10R/7 and R
9
¼
R/5; the simulated floating inductance has


























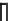

















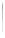


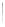














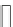































































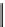
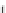



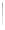




















































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search