Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
shape comparison [
102
], the average geodesic distance has been used for shape decomposition
and segmentation [
110
,
177
], surface parameterization and texture mapping [
214
], symmetry
analysis [
114
], partial matching [
178
,
197
].
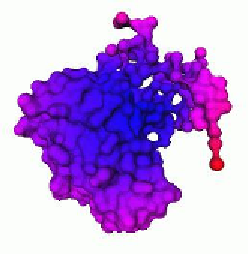
Figure 4.2:
e behavior of the average geodesic function: the value of the function is colored from
low (blue) to high (red).
4.2 CURVATURE ON SURFACES
Another property, used frequently in shape analysis, is curvature which appears in a variety of
flavors in applications. For surfaces, two kinds of curvature are considered:
Gaussian curvature
and
mean curvature
. ey are defined using the
principal curvatures
, which measure the maximum
and minimum bending in different directions of a regular surface at each point. More precisely,
at each point
p
of a differentiable surface in a 3-dimensional Euclidean space one may choose
a unit normal vector. Each plane through
p
that contains the normal intersects the surface in a
plane curve. is curve will in general have different curvatures for different normal planes at
p
.
³
e extremal values, namely the
maximal curvature
k
1
and the
minimal curvature
k
2
, are called
the
principal curvatures
of the surface at
p
. A curvature is taken to be positive if the curve turns
in the same direction as the surface normal, otherwise it is taken to be negative.
Figure
4.3
represents the principal curvatures
k
1
and
k
2
and the normal vector
En
at a saddle
point.
e
Gaussian curvature
K
, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, is the product of the prin-
cipal curvatures:
KDk
1
k
2
:
e
mean curvature
H
is half the sum of the principal curvatures:
HD
1
2
.k
1
Ck
2
/:
³Recall that the curvature of a planar curve at a pointpis by definition the reciprocal of the radius of the osculating circle,
which is the unique circle or line which most closely approximates the curve nearp.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search