Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
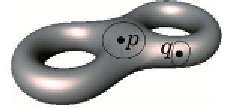
Figure 3.5:
From left to right: neighbors of points on a
2
-manifold without boundary and a
2
-
manifold with boundary. In the last example, the neighbors of the points that lie in the intersection of
the bitorus with a plane are not homeomophic to any disk and therefore the surface is non-manifold
[
217
].
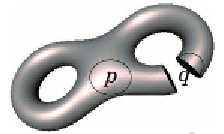
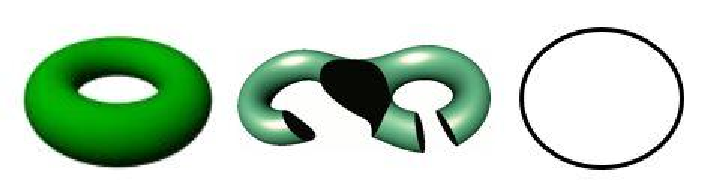
Figure 3.6:
From left to right: a
3
-manifold with boundary, a
2
-manifold with boundary and a
1
-
manifold without boundary (a circle) [
217
].
3.6
CHARTS
Points on manifolds have a local neighborhood structure, which can be exploited to build a kind
of local representation of the manifold itself. As curves can be parametrized by arc length, here
we may construct a step-wise representation of the manifold by associating a homeomorphism
'
i
WU
i
!D
k
to each open subset
U
i
.
Each pair
.U
i
;'
i
/
is called a
map
, or a
chart
, while the union of charts
f.U
i
;'
i
g
is called
the
atlas
on the manifold
M
. e terminology used here clearly reflects the meaning of these
concepts: the most natural intuition we may think of are the atlases for representing the Earth.
To use charts when reasoning in the smooth domain, we need to ensure that smoothness
while moving from one chart to another. For this, we need to introduce the concept of
transition
function
to each atlas on a manifold. Let
U
i
,
U
j
be two arbitrary charts and
U
i
\U
j
be their
intersection. On this intersection two coordinate maps
'
i
WU
i
\U
j
!'
i
.U
i
\U
j
/D
k
and
'
j
WU
i
\U
j
!'
j
.U
i
\U
j
/D
k
are defined. Since the composition of homeomorphisms is
a homeomorphism, the homeomorphisms
'
i;j
W'
i
.U
i
\U
j
/!'
j
.U
i
\U
j
/
such that
'
i;j
D
'
j
\'
i
are well defined on the open subset
'
i
.U
i
\U
j
/D
k
and are called
transition functions
or
gluing functions
on a given atlas.
1

Search WWH ::

Custom Search