Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
K
‐means clustering algorithm does improve both ice type
and ice‐OW discrimination. They also found that subse-
quent processing using the Markov random field (MRF)
labeling model improves the image segmentation signifi-
cantly. The advantage of this method lies in its ability to
incorporate spatial information of gray tone into a seg-
mentation process. Therefore, it can be used as a labeling
model to identify segmented regions. An example of the
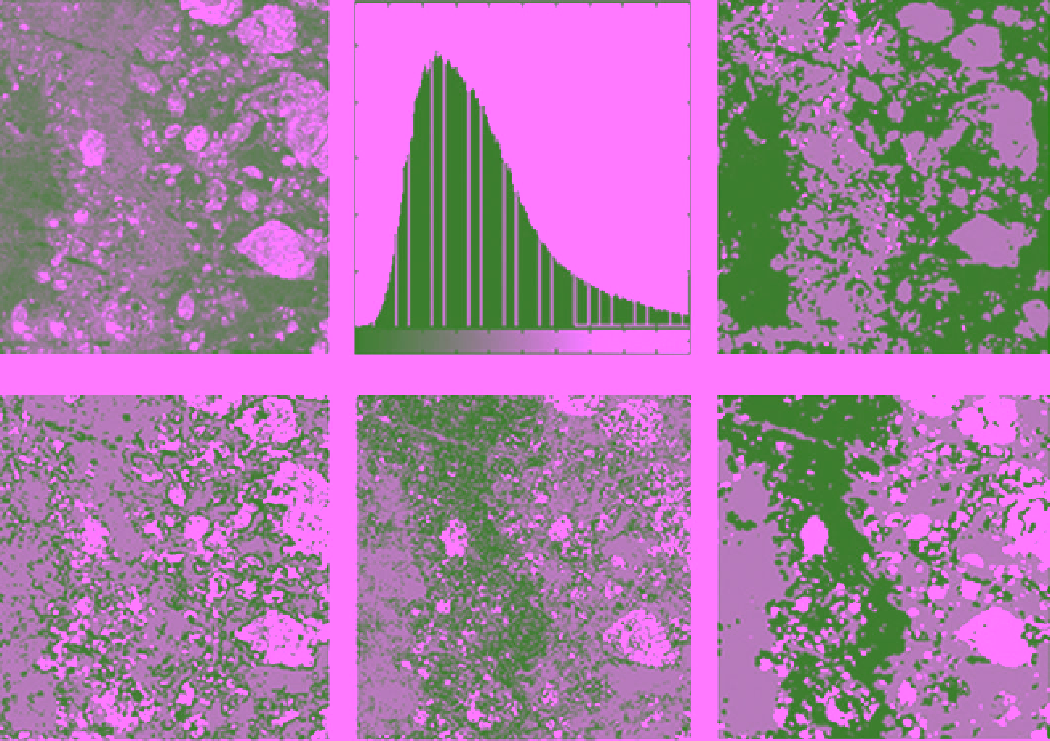
results from their work is presented in Figure 10.3. The
scene was acquired in the middle of winter (7 February
1998) in northern Baffin Bay and contains three ice types:
gray, gray‐white and MYI. The histogram of the image
gray tone shows a unimodal distribution (Figure 10.3b),
which makes it difficult to segment the image using a
computer vision technique. As shown in Figure 10.3c, it is
obvious that the gray tone will not achieve proper image
segmentation. This image was produced using the finite
gamma mixture model. Only two of the three ice classes
are identified because MY ice and gray‐white ice have
similar gray tone values. The result from another segmen-
tation approach using texture only (GLCM measures fol-
lowed by
K
‐means clustering) is shown in Figure 10.3d.
In this case, gray ice and gray‐white ice are erroneously
grouped together and MYI is identified as a separate
class. Figure 10.3e represents a segmentation based on
a fused feature set (GLCM texture + tone) followed by
K
‐means clustering. In this case all three ice classes are
identified though not accurately. When the MRF label
model is applied to the result in Figure 10.3e the best
segmentation result emerges as presented in Figure 10.3 f.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
Figure 10.3
Radarsat‐1 SAR (a) sea ice image of a northern area of Baffin Bay, acquired 7 February 1998, with (b) the
histogram of image in 8‐bit gray tone scale. (c) Segmentation based on gray tone only using gamma mixture model.
(d) Segmentation based on texture only using GLCM and
K
‐means clustering. (e) Segmentation based on fused texture
and tone with
K
‐means clustering. (f) An improved segmentation with application of gamma MRF model. Three ice
types are represented in segmented images by colors: gray ice in black, gray‐white ice in gray color, and MYI ice in
white [adapted from
Calusi and Deng
, 2003, Figure 4, with permission from IEEE].