Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
0.0
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
20
40
60
Snow depth (cm)
80
100
0.00
-0.05
100-.03
200-.03
300-.03
400-.03
100-.12
-0.10
200-.12
300-.12
400-.12
-0.15
100-.21
200-.21
300-.21
400-.21
100-.30
200-.30
300-.30
400-.30
-0.20
20
40
60
Snow depth (cm)
80
100
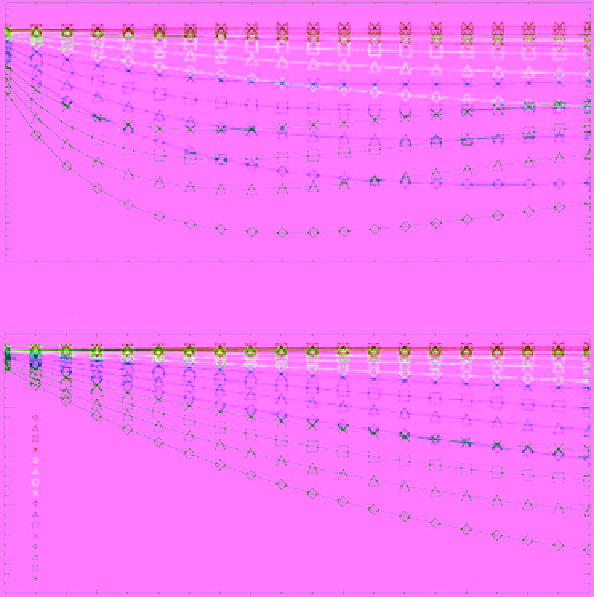
Figure 7.43
Variation of the gradient ratio (vertical polarization) of 37/19 GHz (top) and 19/10 GHz (bottom)
versus snow depth for several snowpack densities and correlation lengths. The first number in the legend is the
density (in kg/cm
3
), corresponding to the different symbols, while the second number is the correlation length
(in millimeters), corresponding to the different colors [
Powell et al
., 2006, Figure 2, with permission from IEEE].
(For color detail, please see color plate section).
5
Multiple scattering model
First-order scattering model
Second-order scattering model
Multiple scattering model
First-order scattering model
Second-order scattering model
0
0
-10
-5
-20
-10
-30
-15
-40
VV polarization
VH polarization
-20
-50
0.0
0.5
1. 0
1.5
2.0
0.0
0.5
1. 0
1.5
2.0
Radius (mm)
Radius (mm)
Figure 7.44
Simulated volume backscattering coefficient calculated from the first‐ and second‐order scattering
models as well as a multiple scattering model presented in
Du et al.
[2010] as a function of grain size in snow-
pack. Calculations are performed for snow‐water equivalent of 100 mm at frequency 17 GHz and incidence angle
40° [
Du et al
., 2010, Figure 4, with permission from Elsevier].