Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
[82
Lin
—
0.4
——
Nor
PgE
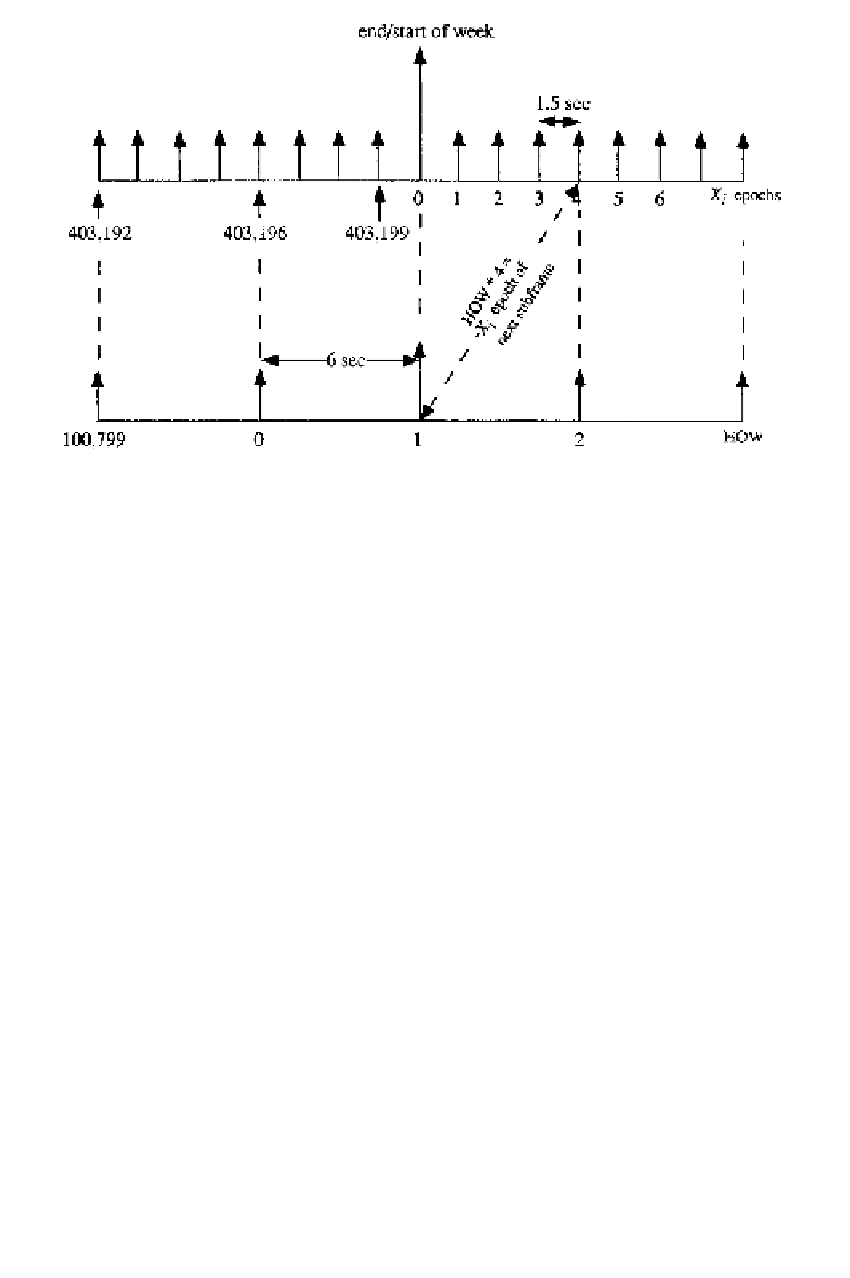
Figure 3.11
HOW versus
X
1
epochs.
issue of data ephemeris (IODE) term allows users to detect changes in the ephemeris
parameters. For each upload, the control center assigns a new number. The IODE is
given in both subframes. During the time of an upload, both IODEs will have different
values. Users should download ephemeris data only when both IODEs have the same
value. The broadcast elements are used with the algorithm of Table 3.6. The results are
coordinates of the phase center of the space vehicle's antennas in the World Geodetic
System of 1984 (WGS84). The latter is an ECEF coordinate system that is closely
aligned with the international terrestrial reference frame (ITRF). There is no need for
an explicit polar motion rotation, since the respective rotations are incorporated in
the representation parameters. However, when computing the topocentric distance,
the user must account for the rotation of the earth during the signal travel time from
satellite to receiver.
Subframes 4 and 5 contain special messages, ionospheric correction terms, coeffi-
cients to convert GPS time to universal time coordinated (UTC), and almanac data on
pages 2-5 and 7-10 (subframe 4) and 1-24 (subframe 5). The ionospheric terms are
the eight coefficients
[82
{α
β
n
}
referenced in Table 6.3. For accurate computation of
UTC from GPS time, the message provides a constant offset term, a linear polynomial
term, the reference time
t
ot
, and the current value of the leap second. The almanac pro-
vides data to compute the positions of satellites other than the transmitting satellite. It
is a reduced-precision subset of the clock and ephemeris parameters of subframes 1
to 3. For each satellite, the almanac contains the following:
t
oa
,
n
,
Ω
,
a
1
/
2
,
δ
i
,
a
f
0
,
a
f
1
,
e
,
Ω
0
,
, and
M
0
. The almanac reference time is
t
oa
. The correction to the inclination
δ
i
is given with respect to the fixed value
i
0
=
ω
54°). The clock
polynomial coefficients
a
f
0
and
a
f
1
are used to convert space vehicle (SV) time to
GPS time, following Equation (5.38). The remaining elements of the almanac are
0
.
30 semicircles (
=