Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
[33
Lin
—
0.1
——
Lon
PgE
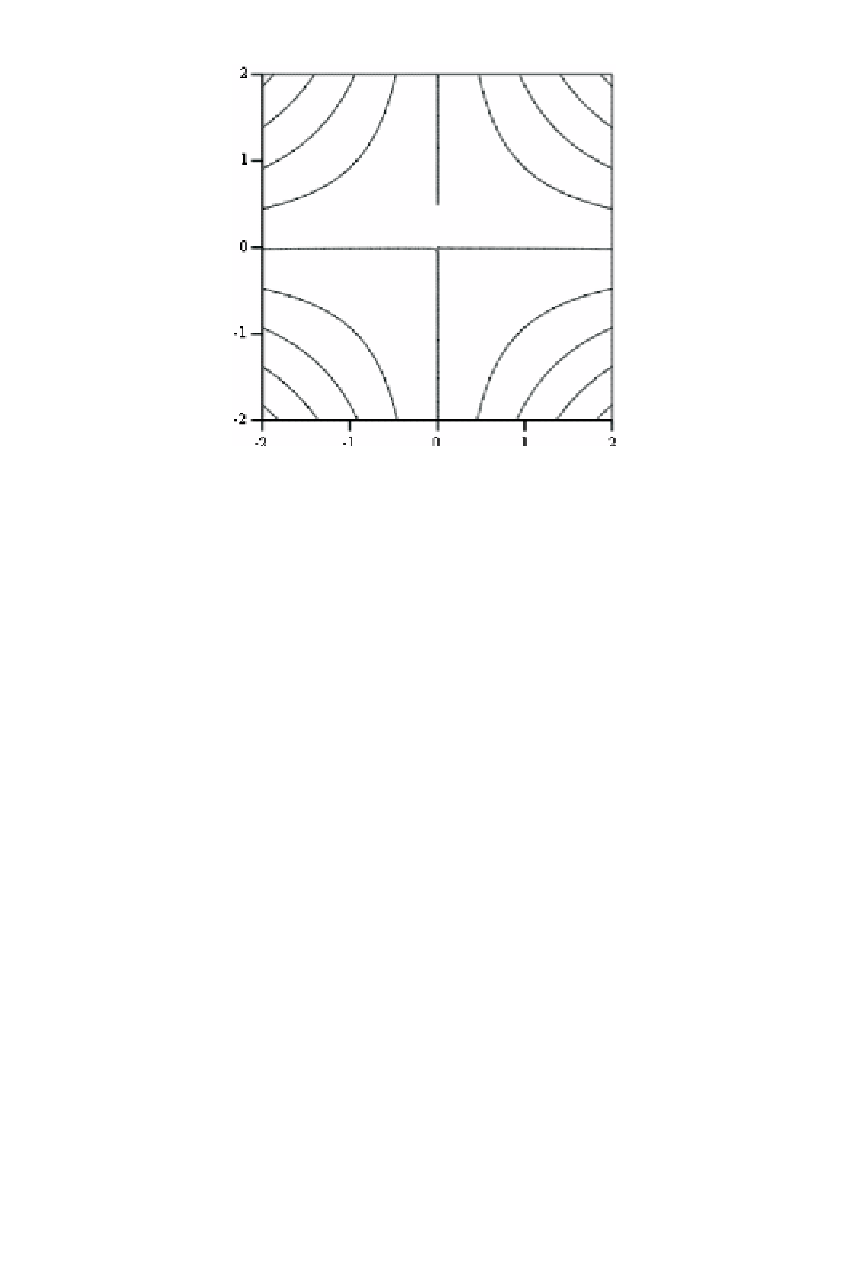
Figure 9.6
Comparing GML functions minus linearized form.
Contour increment is 1/10 mm.
0.4 mm in the northwest and northeast corners. There is an agreement to better than 1
mm within the test area. The shape of the contour lines changes even with the sign of
the differentials
(dϕ
i
,d
λ
i
)
. This figure, therefore, serves only as an example of what
discrepancies to expect for differentials of 1 m. There is a proportional relationship
between the magnitude of the discrepancies and the magnitude of the differentials,
at least for reasonable values of the differentials. For example, differentials of 10 m
cause discrepancies in the range of 4 mm. Since it is easy to establish approximate
coordinates of about 1 m with GPS, we can readily state that GML functions and the
differentials are consistent within 1 mm in the 4°
[33
×
4° test area.
9.2 THE CONFORMAL MAPPING MODEL
If the goal is to map the ellipsoid onto a plane in order to display it on the computer
screen or to assemble overlays of spatial data, any unique mapping from the ellipsoid
to the plane may be used. In conformal mapping, we map the ellipsoidal surface con-
formally onto a plane. The conformal property preserves angles. An angle between
two curves, say, two geodesics on the ellipsoid, is defined as the angle between the
tangents on these curves. Therefore, conformal mapping preserves the angle between
the tangents of curves on the ellipsoid and the respective mapped images. The confor-
mal property makes conformal maps useful for computations because the directional
elements between the ellipsoid and the map have a known relationship.
Users who prefer to work with plane mapping coordinates rather than geodetic
latitude and longitude can still use the 3D adjustment procedures developed in Chap-
ter 2. The given mapping coordinates can be transformed to the ellipsoidal and then
used, together with heights, in the 3D geodetic adjustment. The adjusted geodetic