Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
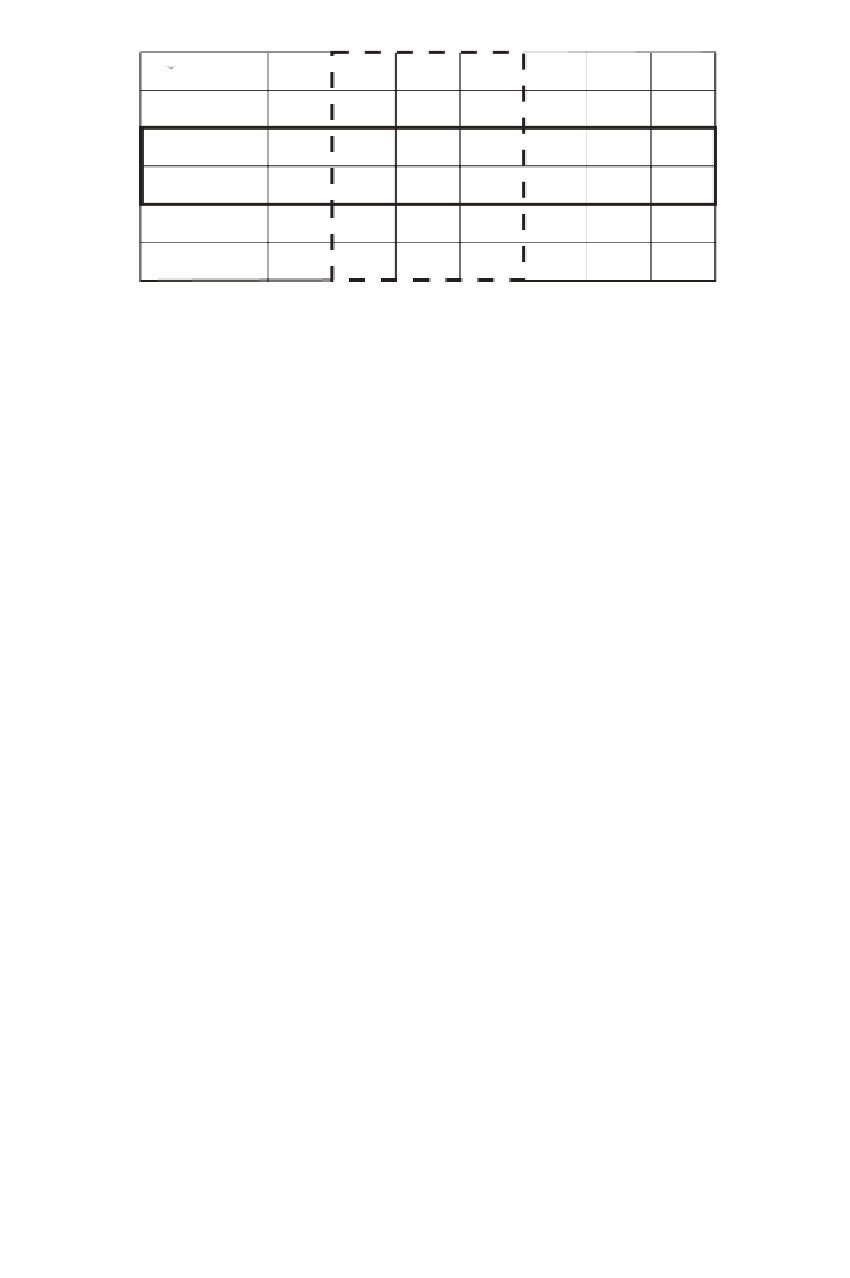
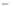
TABLE 7.3
Specification of the D Matrix
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
3. The matrix
˘
Iisofsize3by4.
Note: R
=
3,
S
=
4,
T
=
[26
∇
1
.
∇
T
−
1
Lin
—
0
——
No
*PgE
∇
=
(7.86)
∇
=
T
∆
=
TD
ψ
(7.87)
The matrix
T
might be called the epoch differencing coefficient matrix transforming
double differences to triple differences. The product matrix
TD
might be called the
triple-difference coefficient matrix that transforms single differences directly into
double differences. The pattern of the
T
matrix is seen in Table 7.4. Each baseline
adds one row and each epoch adds one column to this matrix.
The double- and the triple-difference observations are linear functions of the ob-
served carrier phases. By applying covariance propagation and taking the cofactor
matrix (7.80) into account, the respective cofactor matrices are
[26
ϕ
DD
T
Q
∆
= σ
(7.88)
TQ
∆
T
T
Q
∇
=
(7.89)
The double-difference cofactor matrix
Q
∆
is block-diagonal. The diagonal submatrix
in the case of
R
=
3 and
S
=
4is
TABLE 7.4
Specifications of the T Matrix
I
I
I
I
Note: R
=
3,
S
=
4,
T
=
3. The matrix
I
is of size 6