Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
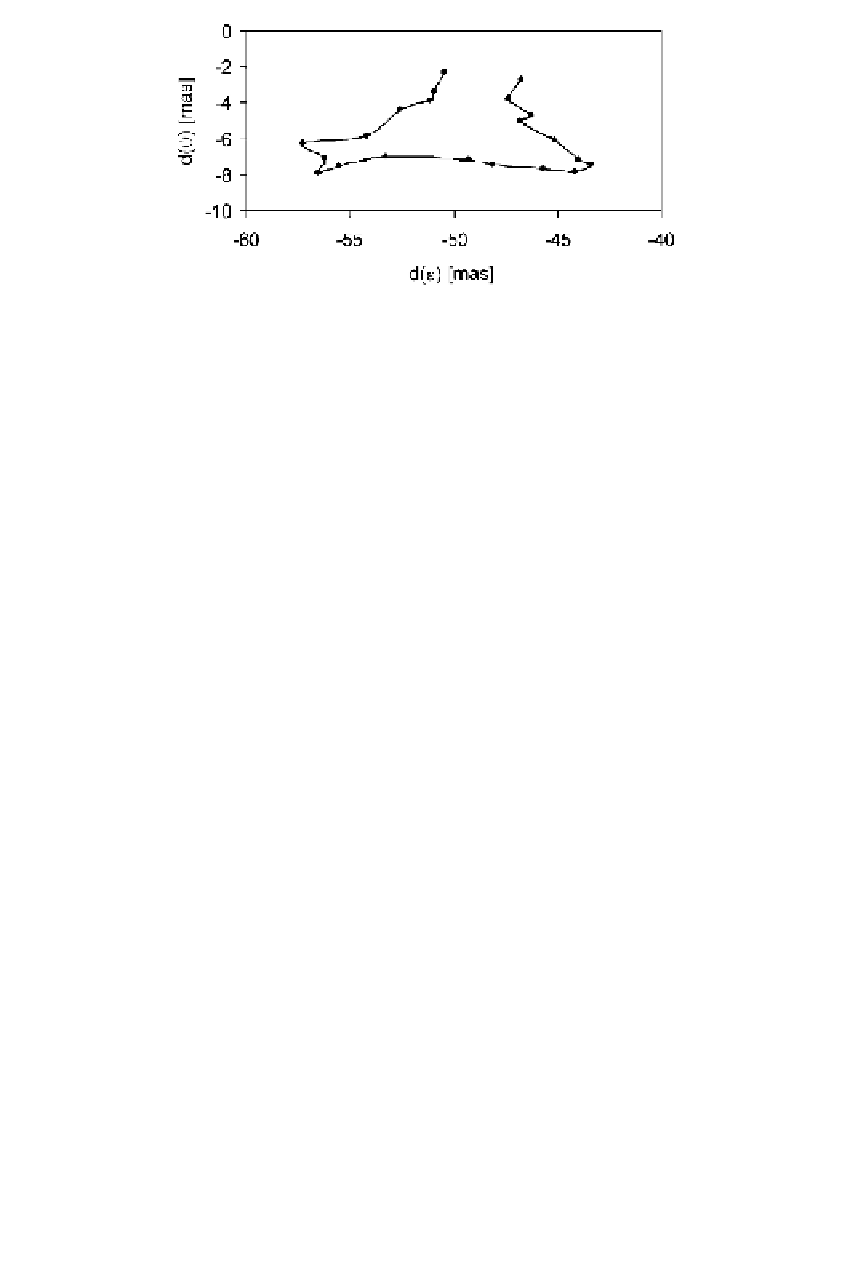
Figure 2.5 Celestial pole offset for 1999 with respect to the IAU 1980 Nutation Model.
(D
ata from 1999 IERS Annual Report.)
[23
m
odel is replacing the IAU 1980 theory of nutations. Because any model is imperfect
an
d imperfections become noticeable as the observation accuracy increases, the so-
ca
lled celestial pole offsets
d
Lin
—
1.3
——
No
*PgE
ψ
and
dε
have been added to (2.18) and (2.19). These
of
fsets are determined and reported by the IERS. An example is seen in Figure 2.5.
The element
also describes the 18.6-year tidal period. Because tides and nutation
are caused by the same gravitational attraction, it is actually possible to transform the
mathematical series of nutations into the corresponding series of tides. Therefore,
Expression (2.5) could be developed into a series of sine and cosine terms with the
fundamental periodic elements as arguments. These elements are
Ω
[23
l
=
Mean Anomaly of the Moon
(2.21)
1717915923
.
2178
t
31
.
8792
t
2
0
.
051635
t
3
=
134°
.
96340251
+
+
+
+···
l
=
Mean Anomaly of the Sun
(2.22)
12596581
.
0481
t
0
.
5532
t
2
0
.
000136
t
3
=
357°
.
52910918
+
−
−
+···
F
=
L
− Ω
(2.23)
1739527262
.
8478
t
12
.
7512
t
2
0
.
001037
t
3
=
+
−
−
+···
93°
.
27209062
D
=
Mean Elongation of the Moon from the Sun
(2.24)
1602961601
.
2090
t
6
.
3706
t
2
0
.
006593
t
3
=
297°
.
85019547
+
−
+
+···
Ω =
Mean Longitude of the Ascending Node of the Moon
(2.25)
6962890
.
2665
t
7
.
4722
t
2
0
.
007702
t
3
=
125°
.
04455501
−
+
+
+···
L
is mean longitude of the moon. In these equations, the time
t
is measured in Julian
centuries of 36,525 days since J2000.0,