Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Partition 1
Partition 2
Partition 3
Partition 4
Partition 5
51
34
12
8
6
9
9
7
10
8910
6
4512
2345
678
9
25 21 22
51
2
910
67
8910
45
23 24 25
3
Partition 1
Partition 2
Partition 3
Partition 4
Partition 5
1
2
3
678
20 17 18 19
18 19 20 16 17
16
45
1
9106 7
3
78
910161718
19 20
1
2
3
4
10
67
8
19
20
13 14 15
11 12 13
14
16
17
18
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
1511
7
8910
67
1
2
3
45
1
12 13 14
10
678910
4
5
1
23
4
15 11 12
8
9106 78
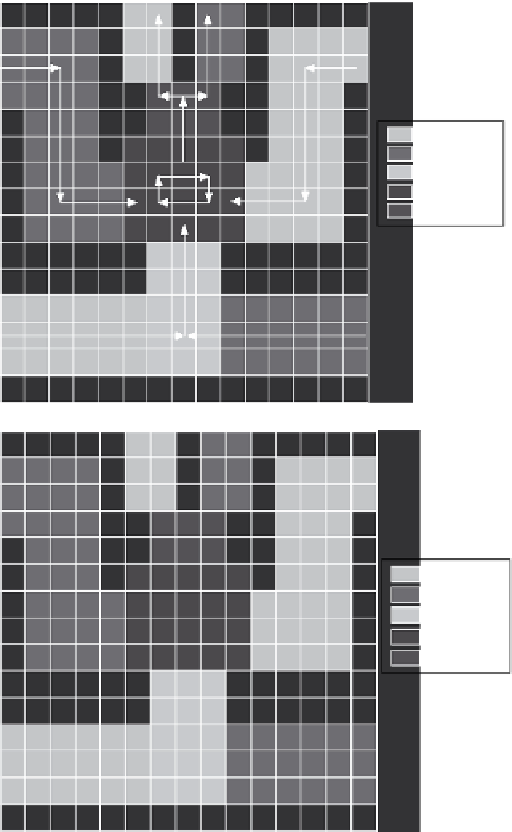
Figure 3.12
Partition and pin-assignment results of the multiplex bioassay. Blank areas are “don't-care”
regions that can be either left unaddressed or combined with any partition.
belongs to are selected, as shown in Figure 1.3. This cross-reference method
facilitates the reduction of control pins. However, due to electrode interfer-
ence, this design cannot handle the simultaneous movement of more than
two droplets. The resulting serialization of droplet movement is a serious
drawback for high-throughput applications.
As discussed in Chapter 1 (Section 1.2), the minimization of the assay comple-
tion time, that is, the maximization of throughput, is essential for applications
such as environmental monitoring, surgery, and neonatal clinical diagnostics.