Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Detector1(x, y)
Detector2(x, y)
Detector3(x, y)
Droplet 1
(8, 3)
(8, 9)
(5, 9)
Droplet 2
(3, 2)
(3, 6)
(5, 6)
(a)
Y
9
8
7
6
Partition 1
5
4
3
2
Partition 2
Droplet Trace
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
X
(b)
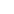
Figure 3.4
(a) Detectors used in bioassay; (b) routing result and array partitions.
Based on this requirement, we find that the droplet trace, defined as the
set of cells traversed by a single droplet, serves as a good tool for generating
the array partitions. Since we view pin assignment as the last step in sys-
tem synthesis, information about module placement and droplet routing is
available a priori. The droplet trace can be easily extracted from the droplet-
routing information and the placement of the modules to which it is routed.
A trace extraction example is shown in Figure 3.4, where two droplets are to
be manipulated on the microfluidic array. Both of these are required to be
detected by an optical sensor three times in a specific bioassay. The place-
ment of these detectors is shown in Figure 3.4a. The droplet routes, that is,
the path taken by droplets, are shown by the arrows in Figure 3.4b. The con-
nected arrows illustrate the traces of the two droplets. For each droplet, we
create a partition composed of all the cells on its trace as well as the cells
adjacent to the trace. The adjacent cells are included to form a “guard ring”
along the trace to avoid inadvertent mixing and movement. The guard rings
are a consequence of the fluidic constraint described in [27].
Note that in Figure 3.4b, there are two “white” regions that belong to nei-
ther partition. They are referred to as “don't-care” regions because they are
similar to the don't-care terms in logic synthesis; they can either be assigned
to any partition, or they can together form an additional partition if multi-
droplet operation modules (e.g., mixers) can be positioned in them. In order
to reduce the number of partitions, we introduce a time-division pin-sharing
method. The basic idea is to merge partitions that have no overlapping time
spans, where a time span for a partition is defined as the period of time