Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Electrode connected to the
capacitive sensing circuit
Circuit
output
Normal
Insensitive
Oversensitive
(a)
(b)
Figure 4.29
Test outcomes for the capacitive sensing circuit.
Pivots
(a)
(b)
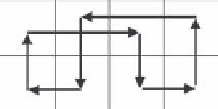
Figure 4.30
(a) Pivots and (b) routing path for a 2 × 4 microfluidic mixer.
Capacitive sensing circuit
connected to this electrode
for Group I
Group V
Group III
Group I
Group II
Group IV
Figure 4.31
Example of the merging test.
mixing test can be reduced to a droplet-merging test, which checks a series of
three adjacent electrodes to determine whether two droplets can be merged
on them. For a microfluidic array, a simple test method carries out droplet
merging on every group of three adjacent electrodes, one at a time. For such
a three electrode test, the test outcome is read out using a capacitive sensing
circuit connected to the center electrode, on which droplets are supposed
to be merged, as shown in Figure 4.31. However, since every electrode can