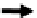Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Source
Source
Sink
Sink
(a)
(b)
Source
Source
Sink
Sink
(c)
(d)
Source
Sink
(e)
Figure 4.7
Step 3: (a) parallel scan-like test for odd rows; (b) routing of test droplets to sink; (c) test
droplet routed to even rows; (d) parallel scan-like test for even rows; (e) routing of test droplets
to sink.
in this work. We only distinguish between a defect involving one cell and
a defect involving two cells, that is, an electrode short. We next present an
efficient diagnosis procedure based on parallel scan-like testing.
For defect-free chips, test droplets, which start simultaneously at the cor-
responding pseudosources, traverse their target columns/rows and reach
their pseudosinks at the same time. The droplets are then routed from the
pseudosinks to the sink, trigging a pulse sequence, as shown in Figure 4.4b.
If there is a defect in a row or a column, the corresponding droplet will not
arrive at the pseudosink. Different pulse patterns correspond to different