Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Biocompatibility
and toxicity
Specic tissue
targeting
Physicochemical
characteristics
and stability
Endoepithelial
barriers crossing
Cell internalization
Drug
loading
Biodistribution
Controlled
drug release
PK
c.a. for
MRI
Label for
uorescence
microscopy
mo
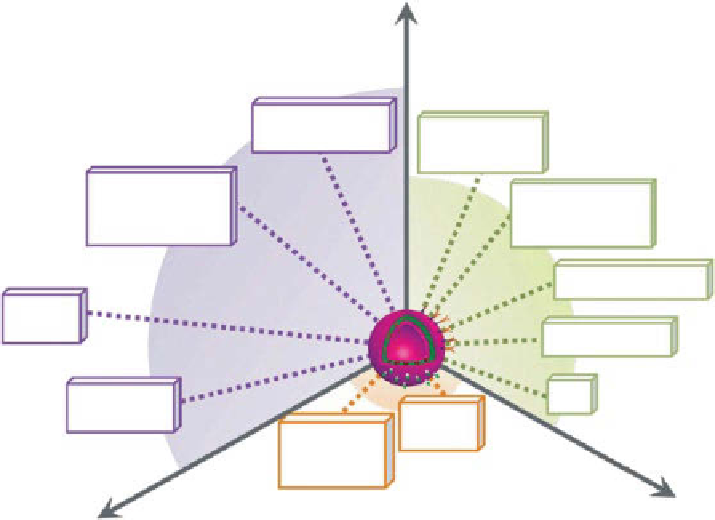
figure 15.8
Challenges of polymersome development for theranostic applications. size
of the branches is proportional to the number of articles dealing with the subject in a logarithmic
scale. (reprinted from ref. [160]. © Wiley.)
theranostic platform through specific examples. We also discuss how polymers may
offer a solution to highly pressing problem of cost and manufacturing of theranostic
nanomedicines. Challenges polymerasomes are to solve are presented in Figure 15.8,
which also illustrates challenges ahead of us regardless of which nanosystem we
are designing.
polymeric particles have been formulated to serve as imaging agents alone for
Mri, optical imaging, and ultrasound or in combination with varied drugs as poten-
tial theranostic systems [161]. it is important to ask a question here: if a polymeric
nanoparticle carrying a drug carries a fluorescent dye that cannot be used for
in vivo
imaging, does this particle qualify as a theranostic? Though we do not wish
to argue against much work done in this way, it is important to keep a perspective
of what true theranostic is. Therefore, here we only discuss those polymeric particles
that can be imaged
in vivo
. nir
in vivo
imaging (discussed earlier in this text) became
a cost-effective and highly versatile imaging method for preclinical and more recently
clinical applications. nir dyes can be directly conjugated to polymers [162] or
incorporated into the nanoparticle by entrapment [154, 163]. For example, Zheng
et al
. doped indocyanine green (iCg), the only FDa-approved nir dye, into
poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (plga) lipid nanoparticles [163]. The resulting
nir nanoparticles exhibited good biocompatibility, monodispersity, excellent nir
Search WWH ::

Custom Search